49844 - Ad-Dukhaan
DAILY MOTIVATION ................... lebih
Dakwah Knowledge
Geo - Mosque News & Stay ... more
Hist - Masjid Berita & Tetap ...
![]() V: 531-532 Panduan Pengguna H:
V: 531-532 Panduan Pengguna H:
11-12
_______________________________
______________________________________________

______________________________________________
______________________________________________
Tafsir Muyassar tafsiran fasilitator
Saheeh International
Basmeih
Ma Jian
E ...... ARAB: ENGLISH: ENGLISH: CHINESE
Interpretasi Tafsir Muyassar Fasilitator: Saheeh International: Basmeih: Ma Jian
_____________________________________________
Celik Tafsir
_____________________________________________
Tafsir Muyassar: tafsiran fasilitator
_____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Saheeh International
___________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Basmeih
______________________________________________
____________________________________________
Ma Jian
_____________________________________________
_______________________________________________
E ...... ARABIC: ENGLISH: ENGLISH: CHINESE
Tafsir Muyassar تفسير المیسر: Saheeh International: Basmeih: Ma Jian
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
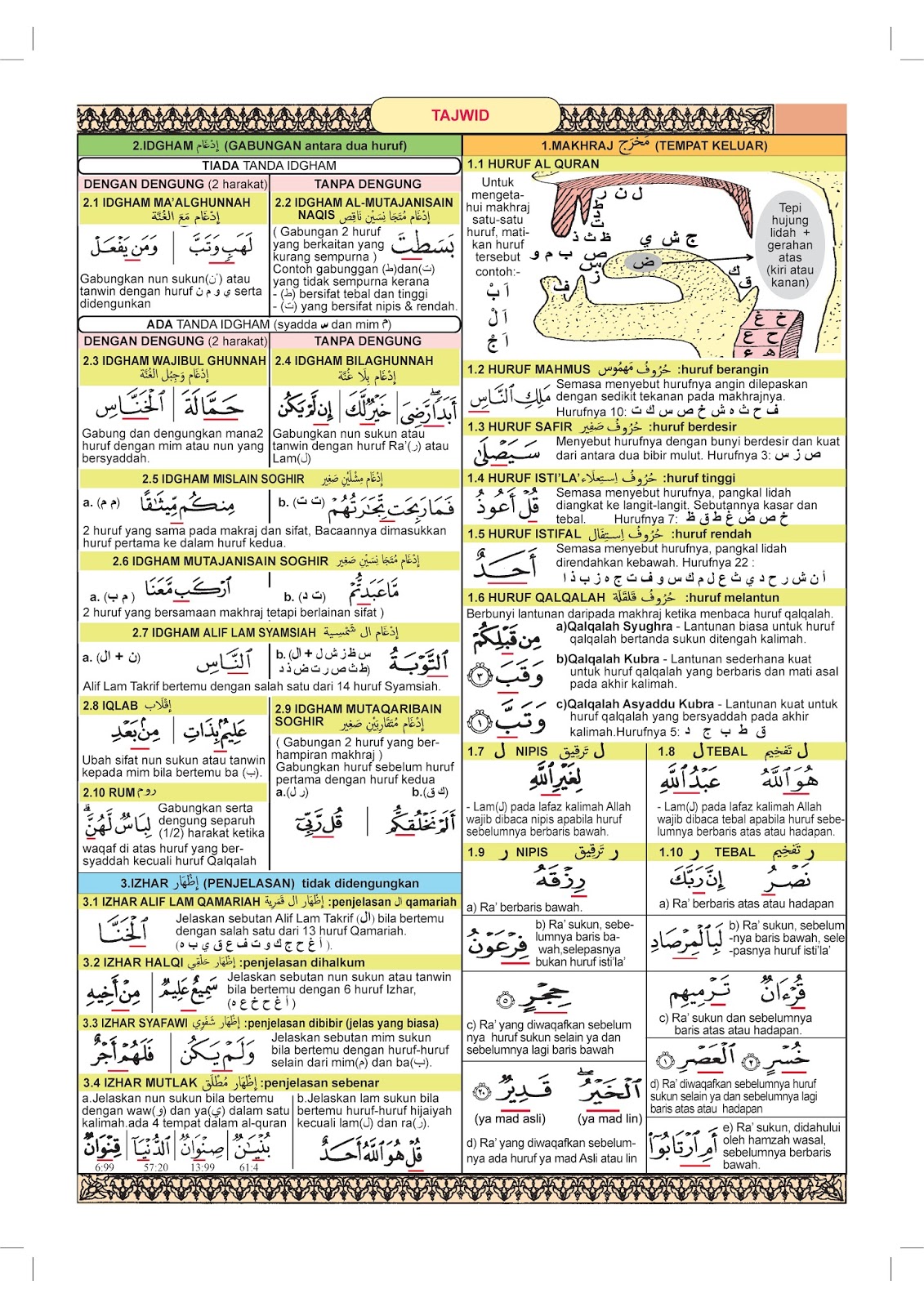
3. LEARN ARABIC: OTHER LANGUAGES




|
فعل
مجهول
مضارع |
فعل
مجهول
ماض |
فعل
معلوم
مضارع |
فعل
معلوم
ماض |
|
|
يفعل |
فعل |
يفعل |
فعل |
I |
|
يفعل |
فعل |
يفعل |
فعل |
II |
|
يفاعل |
فوعل |
يفاعل |
فاعل |
III |
|
يفعل |
أفعل |
يفعل |
أفعل |
IV |
|
يتفعل |
تفعل |
يتفعل |
تفعل |
V |
|
يتفاعل |
تفوعل |
يتفاعل |
تفاعل |
VI |
|
ينفعل |
أنفعل |
ينفعل |
إنفعل |
VII |
|
يفتعل |
أفتعل |
يفتعل |
إفتعل |
VIII |
|
يفعل |
أفعل |
يفعل |
إفعل |
IX |
|
يستفعل |
أستفعل |
يستفعل |
إستفعل |
X |
|
مصدر |
فعل
النهي |
فعل
الأمر |
|
|
فعل |
لاتفعل |
إفعل |
I |
|
تفعيل |
لاتفعل |
فعل |
II |
|
مفاعلة |
لاتفاعل |
فاعل |
III |
|
إفعال |
لاتفعل |
أفعل |
IV |
|
تفعل |
لاتتفعل |
تفعل |
V |
|
تفاعل |
لاتتفاعل |
تفاعل |
VI |
|
إنفعال |
لاتنفعل |
إنفعل |
VII |
|
إفتعال |
لاتفتعل |
إفتعل |
VIII |
|
إفعلال |
|
|
IX |
|
إستفعال |
لاتستفعل |
إستفعل |
X |
|
إسم
الألة |
إسم
المكن
الزمان |
إسم
المفعول |
إسم
الفاعل |
|
|
مفعل |
مفعل |
مفعول |
فاعل |
I |
|
|
مفعل |
مفعل |
مفعل |
II |
|
|
مفاعل |
مفاعل |
مفاعل |
III |
|
|
مفعل |
مفعل |
مفعل |
IV |
|
|
متفعل |
متفعل |
متفعل |
V |
|
|
متفاعل |
متفاعل |
متفاعل |
VI |
|
|
منفعل |
منفعل |
منفعل |
VII |
|
|
مفتعل |
مفتعل |
مفتعل |
VIII |
|
|
مفعل |
مفعل |
مفعل |
IX |
|
|
مستفعل |
مستفعل |
مستفعل |
X |
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
4. ANSWERING CRITIQUES ON ISLAM
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_______________________________________________

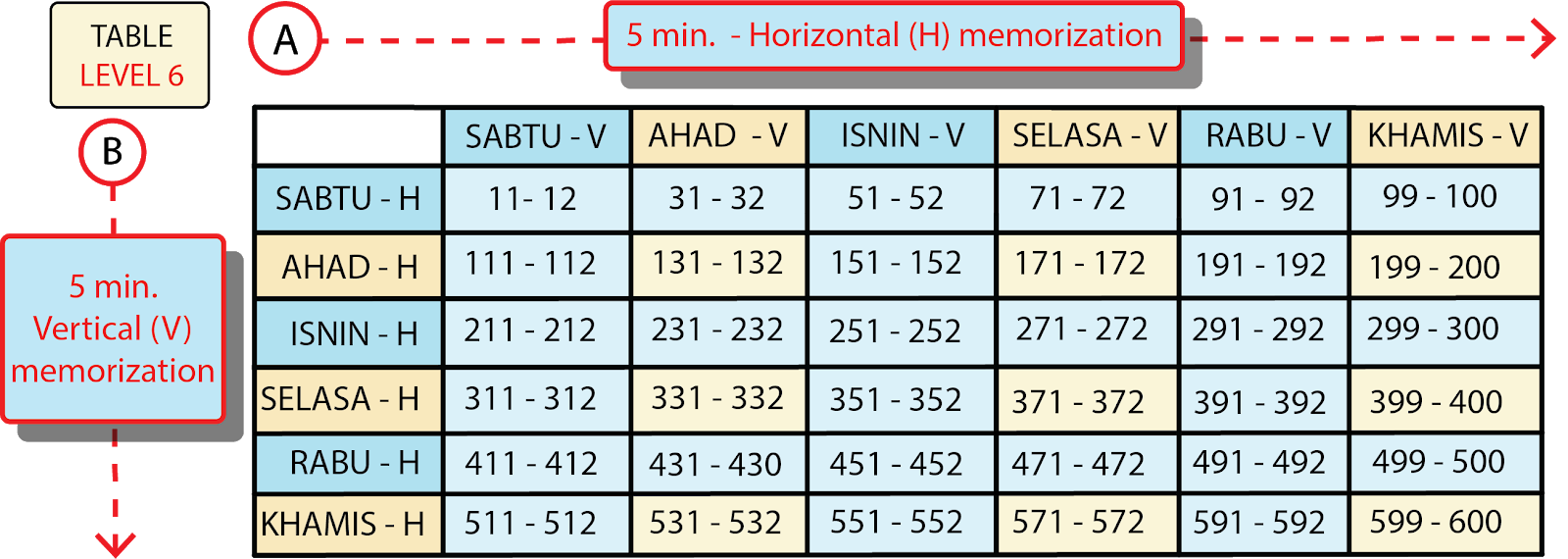
HAFALAN & ULANGAN ...... KAEDAH QAWAN - ada 10 Level
All the Koran in the world is printed on 604 pages. The Qawan Method divides the Qur'an into six parts.
Method of choosing a partner .....
1.Install pages between 2 constituents.
2.The word is not long.
3. Suitable for reading in the first and second rakaat prayers.
4. Suitable for the tazkirah after prayer.
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
LEVEL 1
6 Horizontal Section (Horizontal - H)
Just a pair of pages between 2 constituents.
Saturday: ms 1- 100
Sunday: ms 101 - 200
First Day: pg. 201 - 300
Tuesday: ms 301 - 400
Wednesday: ms 401 - 500
Thursday: ms 501 - 604
Friday: Review all just able
_______________________________________________
6 Vertical Parts (V)
Only the pair of pages (ms) of the entire Qur'an, between 2 constituents that end up with a certain number
H.Sabtu: ms end 01-02
H Sunday: ms end 21-22
H.Nnin: ms end 41-42
H.Selasa: ms end 61-62
H.Rabu: ms end 81-82
H.Khamis: ms end of 99-00
Friday: Review all just able
________________________________________________
LEVEL 2 ..... coming soon
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_____________________________________________
DAILY REMINDER
1. Quran & Hadith
2. Seerah
3. Tabligh 6 points
4. Renowned local preachers
5. Renowned foreign preachers
______________________________________________
1. QURAN & HADITH
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------
1: Al Fatihah: 6
اهدنا الصراط المستقيم
HR Bukhari
وإن أحب الأعمال إلى الله ما دام وإن قل
----------------------------------------
7: Al Baqarah 2: 43
وأقيموا الصلاة وآتوا الزكاة واركعوا مع الراكعين
HR Muslim
صلاة الجماعة أفضل من صلاة الفذ بسبع وعشرين درجة
----------------------------------------
22: Al Baqarah 2: 143
وكذلك جعلناكم أمة وسطا لتكونوا شهداء على الناس ويكون الرسول عليكم شهيدا
HR Ibn Mājah: Sahih (Al-Albani)
"إن الله لا يمل حتى تملوا
--------------------------------------------
52: Ali Imran 3: 19
إن الدين عند الله الإسلام
--------------------------------------
63: Ali Imran 3: 104
ولتكن منكم أمة يدعون إلى الخير ويأمرون بالمعروف وينهون عن المنكر وأولئك هم المفلحون
HR Muslim
من دل على خير, فله مثل أجر فاعله
-----------------------------------------
64: Ali Imran 3: 110
كنتم خير أمة أخرجت للناس تأمرون بالمعروف وتنهون عن المنكر وتؤمنون بالله ....
HR Muslim
من رأى منكم منكرا فليغيره بيده, فإن لم يستطع فبلسانه, فإن لم يستطع فبقلبه, وذلك أضعف الإيمان
-------------------------------------------
74: Ali Imran 3: 185
كل نفس ذائقة الموت
Sunan Ibn Majah ..... Grade Hasan (Darussalam)
ثم قال: يا رسول الله أى المؤمنين أفضل قال: "أحسنهم خلقا". قال فأى المؤمنين أكيس قال: " أكثرهم للموت ذكرا وأحسنهم لما بعده استعدادا أولئك الأكياس "
--------------------------------------------
87: Al Nisaa '4: 59
يا أيها الذين آمنوا أطيعوا الله وأطيعوا الرسول وأولي الأمر منكم فإن تنازعتم في شيء فردوه إلى الله والرسول إن كنتم تؤمنون بالله واليوم الآخر ذلك خير وأحسن تأويلا
HR Imam Malik in Al Muwatta
"تركت فيكم أمرين لن تضلوا ما تمسكتم بهما كتاب الله وسنة نبيه
HR Abu Daud & Termidhi ... Hadith Hasan Sahih
فعليكم بسنتي وسنة الخلفاء الراشدين المهديين.
---------------------------------------------
107: Al Maidah 5: 3
اليوم أكملت لكم دينكم وأتممت عليكم نعمتي ورضيت لكم الإسلام دينا
_____________________________
134: Al An'am 6: 54
.وإذا جاءك الذين يؤمنون بآياتنا فقل سلام عليكم
HR Termizi .... Hadith Hasan Sahih
"يا أيها الناس أفشوا السلام, وأطعموا الطعام, وصلوا الأرحام وصلوا والناس نيام, تدخلوا الجنة بسلام"
--------------------------------------------
342: Al Mu'minun 23: 1-2
1.قد أفلح المؤمنون
2. الذين هم في صلاتهم خاشعون
HR Imam Malik
وأسوأ السرقة الذي يسرق صلاته ". قالوا وكيف يسرق صلاته يا رسول الله قال" لا يتم ركوعها ولا سجودها
-----------------------------------------------
404: Al Ankabut 29: 69
والذين جاهدوا فينا لنهدينهم سبلنا وإن الله لمع المحسنين
420: Al Ahzab 33: 21
لقد كان لكم في رسول الله أسوة حسنة لمن كان يرجو الله واليوم الآخر وذكر الله كثيرا
507: Muhammad 47: 7
يا أيها الذين آمنوا إن تنصروا الله ينصركم ويثبت أقدامكم
560: And Tahrim 66: 6
أنفسكم وأهليكم نارا وقودها الناس والحجارة عليها ملائكة غلاظ شداد لا يعصون الله ما أمرهم ويفعلون ما يؤمرون
__________________________________________________
2. HADITH
2: HR Tirmidhi
مفتاح الجنة الصلاة ومفتاح الصلاة الوضوء
19: HR Bukhari
"خيركم من تعلم القرآن وعلمه"
HR Muslim
"إذا مات الأنسان انقطع عمله إلا من ثلاث: صدقة جارية, أو علم ينتفع به, أو ولد صالح يدعو له"
(HR Bukhari & Muslim: muttafaq 'alaih)
اليد العليا خير من اليد السفلى
HR Bukhari
بلغوا عنى ولو اية
__________________________________________________
3. SEARCH
Narrated 'Abdur-Rahman bin' Awf:
that the Messenger of Allah said: "Abu Bakr is in Paradise, 'Umar is in Paradise,' Uthman is in Paradise, 'Ali is in Paradise, Talhah is in Paradise, Az-Zubair is in Paradise,' Abdur- Rahman bin 'Awf is in Paradise, Sa'd bin Abi Waqqas is in Paradise, Sa'eed is in Paradise, and Abu' Ubaidah bin Al-Jarrah is in Paradise. "
حدثنا قتيبة, حدثنا عبد العزيز بن محمد, عن عبد الرحمن بن حميد, عن أبيه, عن عبد الرحمن بن عوف, قال قال رسول الله صلى الله عليه وسلم "أبو بكر في الجنة وعمر في الجنة وعثمان في الجنة وعلي في الجنة وطلحة في الجنة والزبير في الجنة وعبد الرحمن بن عوف في الجنة وسعد في الجنة وسعيد في الجنة وأبو عبيدة بن الجراح في الجنة ".
| Grade | : Sahih (Darussalam) |
| English reference | : Vol. 1, Book 46, Hadith 3747 |
| Arabic reference | : Book 49, Hadith 4112 |
____________________________________________
Narrated Sa'id ibn Zayd:
AbdurRahman ibn al-Akhnas said that when he was in the mosque, a man mentioned Ali (may Allah be pleased with him). So Sa'id ibn Zayd got up and said: I bear witness to the Messenger of Allah (ﷺ) that I heard him say: Ten persons will go to Paradise: The Prophet (ﷺ) will go to Paradise, AbuBakr will go to Paradise , Umar will go to Paradise, Uthman will go to Paradise, Ali will go to Paradise, Talhah will go to Paradise: az-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam will go to paradise, Sa'd ibn Malik will go to Paradise, and AbdurRahman ibn Awf will go to Paradise. If I wish, I can mention the tenth. The People asked: Who is he: So he kept silence. The again asked: Who is he: He replied: He is Sa'id ibn Zayd.
حدثنا حفص بن عمر النمري, حدثنا شعبة, عن الحر بن الصياح, عن عبد الرحمن بن الأخنس, أنه كان في المسجد فذكر رجل عليا عليه السلام فقام سعيد بن زيد فقال أشهد على رسول الله صلى الله عليه وسلم أني سمعته وهو يقول "عشرة في الجنة النبي في الجنة وأبو بكر في الجنة وعمر في الجنة وعثمان في الجنة وعلي في الجنة وطلحة في الجنة والزبير بن العوام في الجنة وسعد بن مالك في الجنة وعبد الرحمن بن عوف في الجنة ". ولو شئت لسميت العاشر. قال فقالوا من هو فسكت قال فقالوا من هو فقال هو سعيد بن زيد.
Grade: Sahih
| Reference | : Sunan Abi Dawud 4649 |
| In-book reference | : Book 42, Hadith 54 |
| English translation | : Book 41, Hadith 4632 |
___________________________________________
History of success in early Islam during the time of the Prophet and Caliph Ar Rasyidin:
Metallic fittings ...... less
Conformity ....... is high
Ten Companions of the Prophet who are guaranteed paradise ..... the rich majority, but generous .... especially Abdurrahman bin Auf RA ..... The FATONAH looking for opportunities to be the above hands
__________________________________
4. TABLIGH 6 POINTS

_________________________________
5. RENOWNED LOCAL PREACHERS
1. Ustaz Azhar Idrus
2. Maulana Asri
3. Dr Rozaimi
4. Mufti Asri Zainul Abidin
5. Ust Kazim
6. Ust Ebit Lew
7. Prof Datuk Dr Muhaya
8. Ust Ismail Kamus
9. Ust Ahmad Dusuki
10. Ust Auni Mohamad
__________________________________
6. RENOWNED FOREIGN PREACHERS
1. Dr Zakir Naik
2. Nouman Ali Khan
3. Mufti Menk
4. Yasmin Mogahed
5. Hussain Yee
6. Omar Suleiman
7. Yusuf Estes
8. Moulana Tariq Jameel
9. Yasir Qadhi
10. Taqi Usmani
__________________________________
Q.500 :272 / 365...Q.498 :270 & 271/365...Q.496: 268 & 269/ 365
٤٩٨
498
Miracle : Quiz
Mukjizat : Kuiz






Tafsir Muyassar تفسير المیسر
Saheeh International
Basmeih
Ma Jian
E......ARABIC : ENGLISH : MALAY : CHINESE
Tafsir Muyassar تفسير المیسر : Saheeh International : Basmeih : Ma Jian
_____________________________________________
Tafsir Muyassar : تفسير المیسر
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
١ قُلْ يَا أَيُّهَا الْكَافِرُونَ
١ قل -أيها الرسول- للذين كفروا بالله ورسوله: يا أيها الكافرون بالله.
٢ لَا أَعْبُدُ مَا تَعْبُدُونَ
٢ لا أعبد ما تعبدون من الأصنام والآلهة الزائفة.
٣ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
٣ ولا أنتم عابدون ما أعبد من إله واحد، هو الله رب العالمين المستحق وحده للعبادة.
٤ وَلَا أَنَا عَابِدٌ مَا عَبَدْتُمْ
٤ ولا أنا عابد ما عبدتم من الأصنام والآلهة الباطلة.
٥ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
٥ ولا أنتم عابدون مستقبلا ما أعبد. وهذه الآية نزلت في أشخاص بأعيانهم من المشركين، قد علم الله أنهم لا يؤمنون أبدًا.
٦ لَكُمْ دِينُكُمْ وَلِيَ دِينِ
٦ لكم دينكم الذي أصررتم على اتباعه، ولي ديني الذي لا أبغي غيره.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
١ إِذَا جَاءَ نَصْرُ اللَّهِ وَالْفَتْحُ
١ إذا تمَّ لك -أيها الرسول- النصر على كفار قريش، وتم لك فتح "مكة".
٢ وَرَأَيْتَ النَّاسَ يَدْخُلُونَ فِي دِينِ اللَّهِ أَفْوَاجًا
٢ ورأيت الكثير من الناس يدخلون في الإسلام جماعات جماعات.
٣ فَسَبِّحْ بِحَمْدِ رَبِّكَ وَاسْتَغْفِرْهُ ۚ إِنَّهُ كَانَ تَوَّابًا
٣ إذا وقع ذلك فتهيأ للقاء ربك بالإكثار من التسبيح بحمده والإكثار من استغفاره، إنه كان توابًا على المسبحين والمستغفرين، يتوب عليهم ويرحمهم ويقبل توبتهم.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
١ تَبَّتْ يَدَا أَبِي لَهَبٍ وَتَبَّ
١ خسرت يدا أبي لهب وشقي بإيذائه رسول الله محمدا صلى الله عليه وسلم، وقد تحقق خسران أبي لهب.
٢ مَا أَغْنَىٰ عَنْهُ مَالُهُ وَمَا كَسَبَ
٢ ما أغنى عنه ماله وولده، فلن يَرُدَّا عنه شيئًا من عذاب الله إذا نزل به.
٣ سَيَصْلَىٰ نَارًا ذَاتَ لَهَبٍ
٣ سيدخل نارًا متأججة، هو وامرأته التي كانت تحمل الشوك، فتطرحه في طريق النبي صلى الله عليه وسلم؛ لأذيَّته.
٤ وَامْرَأَتُهُ حَمَّالَةَ الْحَطَبِ
٤ سيدخل نارًا متأججة، هو وامرأته التي كانت تحمل الشوك، فتطرحه في طريق النبي صلى الله عليه وسلم؛ لأذيَّته.
٥ فِي جِيدِهَا حَبْلٌ مِنْ مَسَدٍ
٥ في عنقها حبل محكم الفَتْلِ مِن ليف شديد خشن، تُرْفَع به في نار جهنم، ثم تُرْمى إلى أسفلها.
_____________________________________________
____________________________________________
Saheeh International
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
١ قُلْ يَا أَيُّهَا الْكَافِرُونَ
1 Say, "O disbelievers,
٢ لَا أَعْبُدُ مَا تَعْبُدُونَ
2 I do not worship what you worship.
٣ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
3 Nor are you worshippers of what I worship.
٤ وَلَا أَنَا عَابِدٌ مَا عَبَدْتُمْ
4 Nor will I be a worshipper of what you worship.
٥ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
5 Nor will you be worshippers of what I worship.
٦ لَكُمْ دِينُكُمْ وَلِيَ دِينِ
6 For you is your religion, and for me is my religion."
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
١ إِذَا جَاءَ نَصْرُ اللَّهِ وَالْفَتْحُ
1 When the victory of Allah has come and the conquest,
٢ وَرَأَيْتَ النَّاسَ يَدْخُلُونَ فِي دِينِ اللَّهِ أَفْوَاجًا
2 And you see the people entering into the religion of Allah in multitudes,
٣ فَسَبِّحْ بِحَمْدِ رَبِّكَ وَاسْتَغْفِرْهُ ۚ إِنَّهُ كَانَ تَوَّابًا
3 Then exalt [Him] with praise of your Lord and ask forgiveness of Him. Indeed, He is ever Accepting of repentance.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
١ تَبَّتْ يَدَا أَبِي لَهَبٍ وَتَبَّ
1 May the hands of Abu Lahab be ruined, and ruined is he.
٢ مَا أَغْنَىٰ عَنْهُ مَالُهُ وَمَا كَسَبَ
2 His wealth will not avail him or that which he gained.
٣ سَيَصْلَىٰ نَارًا ذَاتَ لَهَبٍ
3 He will [enter to] burn in a Fire of [blazing] flame
٤ وَامْرَأَتُهُ حَمَّالَةَ الْحَطَبِ
4 And his wife [as well] - the carrier of firewood.
٥ فِي جِيدِهَا حَبْلٌ مِنْ مَسَدٍ
5 Around her neck is a rope of [twisted] fiber.
___________________________________________
________________________________________________
Basmeih
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
١ قُلْ يَا أَيُّهَا الْكَافِرُونَ
1 Katakanlah (wahai Muhammad): "Hai orang-orang kafir!
٢ لَا أَعْبُدُ مَا تَعْبُدُونَ
2 "Aku tidak akan menyembah apa yang kamu sembah.
٣ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
3 "Dan kamu tidak mahu menyembah (Allah) yang aku sembah.
٤ وَلَا أَنَا عَابِدٌ مَا عَبَدْتُمْ
4 "Dan aku tidak akan beribadat secara kamu beribadat.
٥ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
5 "Dan kamu pula tidak mahu beribadat secara aku beribadat.
٦ لَكُمْ دِينُكُمْ وَلِيَ دِينِ
6 "Bagi kamu ugama kamu, dan bagiku ugamaku".
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
١ إِذَا جَاءَ نَصْرُ اللَّهِ وَالْفَتْحُ
1 Apabila datang pertolongan Allah dan kemenangan (semasa engkau wahai Muhammad berjaya menguasai negeri Makkah), -
٢ وَرَأَيْتَ النَّاسَ يَدْخُلُونَ فِي دِينِ اللَّهِ أَفْوَاجًا
2 Dan engkau melihat manusia masuk dalam ugama Allah beramai-ramai, -
٣ فَسَبِّحْ بِحَمْدِ رَبِّكَ وَاسْتَغْفِرْهُ ۚ إِنَّهُ كَانَ تَوَّابًا
3 Maka ucapkanlah tasbih dengan memuji Tuhanmu dan mintalah ampun kepadaNya, sesungguhnya Dia amat menerima taubat.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
١ تَبَّتْ يَدَا أَبِي لَهَبٍ وَتَبَّ
1 Binasalah kedua-dua tangan Abu lahab, dan binasalah ia bersama!
٢ مَا أَغْنَىٰ عَنْهُ مَالُهُ وَمَا كَسَبَ
2 Hartanya dan segala yang diusahakannya, tidak dapat menolongnya.
٣ سَيَصْلَىٰ نَارًا ذَاتَ لَهَبٍ
3 Ia akan menderita bakaran api neraka yang marak menjulang.
٤ وَامْرَأَتُهُ حَمَّالَةَ الْحَطَبِ
4 Dan juga isterinya, seorang perempuan pemunggah kayu api. -
٥ فِي جِيدِهَا حَبْلٌ مِنْ مَسَدٍ
5 Di lehernya sejenis tali, dari tali-tali yang dipintal.
______________________________________________
____________________________________________
Ma Jian
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ قُلْ يَا أَيُّهَا الْكَافِرُونَ
1 你说:不信道的人们啊!
٢ لَا أَعْبُدُ مَا تَعْبُدُونَ
2 我不崇拜你们所崇拜的,
٣ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
3 你们也不崇拜我所崇拜的;
٤ وَلَا أَنَا عَابِدٌ مَا عَبَدْتُمْ
4 我不会崇拜你们所崇拜的,
٥ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
5 你们也不会崇拜我所崇拜的;
٦ لَكُمْ دِينُكُمْ وَلِيَ دِينِ
6 你们有你们的报应, 我也有我的报应。
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ إِذَا جَاءَ نَصْرُ اللَّهِ وَالْفَتْحُ
1 当真主的援助和胜利降临,
٢ وَرَأَيْتَ النَّاسَ يَدْخُلُونَ فِي دِينِ اللَّهِ أَفْوَاجًا
2 而你看见众人成群结队地崇奉真主的宗教时,
٣ فَسَبِّحْ بِحَمْدِ رَبِّكَ وَاسْتَغْفِرْهُ ۚ إِنَّهُ كَانَ تَوَّابًا
3 你应当赞颂你的主超绝万物, 并且向他求饶, 他确是至宥的。
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ تَبَّتْ يَدَا أَبِي لَهَبٍ وَتَبَّ
1 愿焰父两手受伤!他必定受伤,
٢ مَا أَغْنَىٰ عَنْهُ مَالُهُ وَمَا كَسَبَ
2 他的财产, 和他所获得的, 将无裨于他,
٣ سَيَصْلَىٰ نَارًا ذَاتَ لَهَبٍ
3 他将入有焰的烈火,
٤ وَامْرَأَتُهُ حَمَّالَةَ الْحَطَبِ
4 他的担柴的妻子, 也将入烈火,
٥ فِي جِيدِهَا حَبْلٌ مِنْ مَسَدٍ
5 她的颈上系著一条坚实的绳子。
_____________________________________________
_______________________________________________
E......ARABIC : ENGLISH : MALAY : CHINESE
Tafsir Muyassar تفسير المیسر : Saheeh International : Basmeih : Ma Jian
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ قُلْ يَا أَيُّهَا الْكَافِرُونَ
١ قل -أيها الرسول- للذين كفروا بالله ورسوله: يا أيها الكافرون بالله.
1 Say, "O disbelievers,
1 Katakanlah (wahai Muhammad): "Hai orang-orang kafir!
1 你说:不信道的人们啊!
٢ لَا أَعْبُدُ مَا تَعْبُدُونَ
٢ لا أعبد ما تعبدون من الأصنام والآلهة الزائفة.
2 I do not worship what you worship.
2 "Aku tidak akan menyembah apa yang kamu sembah.
2 我不崇拜你们所崇拜的,
٣ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
٣ ولا أنتم عابدون ما أعبد من إله واحد، هو الله رب العالمين المستحق وحده للعبادة.
3 Nor are you worshippers of what I worship.
3 "Dan kamu tidak mahu menyembah (Allah) yang aku sembah.
3 你们也不崇拜我所崇拜的;
٤ وَلَا أَنَا عَابِدٌ مَا عَبَدْتُمْ
٤ ولا أنا عابد ما عبدتم من الأصنام والآلهة الباطلة.
4 Nor will I be a worshipper of what you worship.
4 "Dan aku tidak akan beribadat secara kamu beribadat.
4 我不会崇拜你们所崇拜的,
٥ وَلَا أَنْتُمْ عَابِدُونَ مَا أَعْبُدُ
٥ ولا أنتم عابدون مستقبلا ما أعبد. وهذه الآية نزلت في أشخاص بأعيانهم من المشركين، قد علم الله أنهم لا يؤمنون أبدًا.
5 Nor will you be worshippers of what I worship.
5 "Dan kamu pula tidak mahu beribadat secara aku beribadat.
5 你们也不会崇拜我所崇拜的;
٦ لَكُمْ دِينُكُمْ وَلِيَ دِينِ
٦ لكم دينكم الذي أصررتم على اتباعه، ولي ديني الذي لا أبغي غيره.
6 For you is your religion, and for me is my religion."
6 "Bagi kamu ugama kamu, dan bagiku ugamaku".
6 你们有你们的报应, 我也有我的报应。
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ إِذَا جَاءَ نَصْرُ اللَّهِ وَالْفَتْحُ
١ إذا تمَّ لك -أيها الرسول- النصر على كفار قريش، وتم لك فتح "مكة".
1 When the victory of Allah has come and the conquest,
1 Apabila datang pertolongan Allah dan kemenangan (semasa engkau wahai Muhammad berjaya menguasai negeri Makkah), -
1 当真主的援助和胜利降临,
٢ وَرَأَيْتَ النَّاسَ يَدْخُلُونَ فِي دِينِ اللَّهِ أَفْوَاجًا
٢ ورأيت الكثير من الناس يدخلون في الإسلام جماعات جماعات.
2 And you see the people entering into the religion of Allah in multitudes,
2 Dan engkau melihat manusia masuk dalam ugama Allah beramai-ramai, -
2 而你看见众人成群结队地崇奉真主的宗教时,
٣ فَسَبِّحْ بِحَمْدِ رَبِّكَ وَاسْتَغْفِرْهُ ۚ إِنَّهُ كَانَ تَوَّابًا
٣ إذا وقع ذلك فتهيأ للقاء ربك بالإكثار من التسبيح بحمده والإكثار من استغفاره، إنه كان توابًا على المسبحين والمستغفرين، يتوب عليهم ويرحمهم ويقبل توبتهم.
3 Then exalt [Him] with praise of your Lord and ask forgiveness of Him. Indeed, He is ever Accepting of repentance.
3 Maka ucapkanlah tasbih dengan memuji Tuhanmu dan mintalah ampun kepadaNya, sesungguhnya Dia amat menerima taubat.
3 你应当赞颂你的主超绝万物, 并且向他求饶, 他确是至宥的。
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
بِسْمِ اللَّهِ الرَّحْمَٰنِ الرَّحِيمِ
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
In the name of Allah, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
Dengan nama Allah, Yang Maha Pemurah, lagi Maha Mengasihani.
奉至仁至慈的真主之名
١ تَبَّتْ يَدَا أَبِي لَهَبٍ وَتَبَّ
١ خسرت يدا أبي لهب وشقي بإيذائه رسول الله محمدا صلى الله عليه وسلم، وقد تحقق خسران أبي لهب.
1 May the hands of Abu Lahab be ruined, and ruined is he.
1 Binasalah kedua-dua tangan Abu lahab, dan binasalah ia bersama!
1 愿焰父两手受伤!他必定受伤,
٢ مَا أَغْنَىٰ عَنْهُ مَالُهُ وَمَا كَسَبَ
٢ ما أغنى عنه ماله وولده، فلن يَرُدَّا عنه شيئًا من عذاب الله إذا نزل به.
2 His wealth will not avail him or that which he gained.
2 Hartanya dan segala yang diusahakannya, tidak dapat menolongnya.
2 他的财产, 和他所获得的, 将无裨于他,
٣ سَيَصْلَىٰ نَارًا ذَاتَ لَهَبٍ
٣ سيدخل نارًا متأججة، هو وامرأته التي كانت تحمل الشوك، فتطرحه في طريق النبي صلى الله عليه وسلم؛ لأذيَّته.
3 He will [enter to] burn in a Fire of [blazing] flame
3 Ia akan menderita bakaran api neraka yang marak menjulang.
3 他将入有焰的烈火,
٤ وَامْرَأَتُهُ حَمَّالَةَ الْحَطَبِ
٤ سيدخل نارًا متأججة، هو وامرأته التي كانت تحمل الشوك، فتطرحه في طريق النبي صلى الله عليه وسلم؛ لأذيَّته.
4 And his wife [as well] - the carrier of firewood.
4 Dan juga isterinya, seorang perempuan pemunggah kayu api. -
4 他的担柴的妻子, 也将入烈火,
٥ فِي جِيدِهَا حَبْلٌ مِنْ مَسَدٍ
٥ في عنقها حبل محكم الفَتْلِ مِن ليف شديد خشن، تُرْفَع به في نار جهنم، ثم تُرْمى إلى أسفلها.
5 Around her neck is a rope of [twisted] fiber.
5 Di lehernya sejenis tali, dari tali-tali yang dipintal.
5 她的颈上系著一条坚实的绳子。
World Islamic History : 498 H
23/9/1104 - 11/9/1105 CE
xxx
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________
xxx
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________
| 652 | Death of Abu Dhar al Ghifari, venerated Companion and Sufi. | |
| 656 | Caliph Uthman bin Affan (r) is assassinated. | |
| Ali ibn Abu Talib (r) is elected the Caliph. | ||
| Beginning of the Civil Wars. | ||
| Caliph Ali ibn Abu Talib (r) defeats dissidents under Aisha binte Abu Bakr (r) at the Battle of the Camel. | ||
| 657 | Muawiya ibn Abu Sufyan, governor of Syria, refuses to recognize the Caliphate of Ali (r). | |
| Battle of Siffin between forces of Ali (r) and Muawiya. | ||
| Beginning of the Kharijite schism. | ||
| 658 | Ali ibn Abu Talib (r) defeats the Kharijites at the Battle of Nahrawan. | |
| Muawiya is declared the Caliph by his supporters in Damascus. | ||
| 659 | Truce between Caliph Ali ibn Abu Talib (r) and Muawiya ibn Abu Sufyan. | |
| 661 | Caliph Ali ibn Abu Talib (r) is assassinated. | |
| Age of Khulfa e Rashidoon ends. | ||
| Muawiya claims the Caliphate. | ||
| Beginning of the Umayyad dynasty. | ||
| Imam Hassan ibn Ali retires from politics. | ||
| 665 | Muawiya orders the buildup of a navy. | |
| 667 | Muslim armies capture Khorasan. | |
| 669 | Death of Imam Hassan ibn Ali. | |
| 670 | Uqba bin Nafi begins the conquest of North Africa. | |
| The city of Kairaoun in North Africa is founded. | ||
| 671 | Muslim armies capture the island of Rhodes. | |
| The first attempt to capture Constantinople fails. | ||
| 678 | Death of Aisha binte Abu Bakr (r), wife of Prophet Muhammed (p) and the source of a large number of Hadith. | |
| 680 | Death of Muawiya ibn Abu Sufyan. | |
| Yazid, son of Muawiya, becomes Omayyad ruler. | ||
| The tragedy of Karbala; Hussain ibn Ali, grandson of the Prophet, is martyred. | ||
| Beginning of Yawm e Ashoora. | ||
| 683 | Yazid sacks Madina. | |
| Uqba bin Nafi conquers North Africa. | ||
| Death of Yazid; Muawiya II succeeds him. | ||
| 684 | Marwan I becomes the Caliph. | |
| 685 | Abdul Malik becomes the Caliph. | |
| Construction of the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem. | ||
| Muslim armies advance into Central Asia. | ||
| 690 | Omayyad armies reach the Atlantic Ocean. | |
| 691 | Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem is completed. | |
| 692 | Abdul Malik mints the first coins of the Islamic state. | |
| 693 | Al Hajjaj, also known as al Hajjaj the cruel, becomes governor of Iraq. | |
| 694 | Construction of the Omayyad Mosque in Damascus. | |
| 699 | Death of Al Juhani, rationalist, philosopher. | |
| back to top | ||
| 705 | Al Walid I becomes the Caliph and begins a vigorous expansion of the empire. | |
| 711 | Tariq ibn Ziyad lands in Spain. Visigoth army under Rodriguez is defeated at the Battle of Buhayrah. | |
| Muhammed bin Qasim lands at Debal, subdues Baluchistan, Sindh, Multan and southern Punjab. | ||
| 712 | Musa ibn Nusair advances into Leon, Astoria and Galicia. | |
| Beginning of 780 years of Muslim rule in Andalus. | ||
| Jewish golden age in Spain. | ||
| Death of Imam Zainul Abedin. | ||
| 713 | Zaid bin Zain ul Abedin organizes resistance to the Omayyads. Beginning of the Zaidi branch. | |
| Muslim armies capture Lyons in France. | ||
| 714 | Muhammed bin Qasim recalled from Sindh by Hajjaj bin Yusuf and imprisoned until death. | |
| Muslims capture Normandy in France. | ||
| 715 | Sulaiman becomes Umayyad Caliph. | |
| Musa ibn Nusair recalled from Spain by Caliph Sulaiman, stripped of all power and banished into the desert. | ||
| 717 | Omar bin Abdul Aziz becomes the Caliph and attempts reconciliation in the Islamic community. He lowers taxes on peasants in Persia and Egypt. | |
| The Byzantines repulse a second Muslim attempt to capture Constantinople. | ||
| Spread of Islam into Persia and Egypt picks up momentum. | ||
| 719 | Omar bin Abdul Aziz is poisoned. | |
| Yazid II becomes the Caliph. | ||
| 720 | Muslim armies cross the Pyrenees and occupy southern France. | |
| 724 | Hisham becomes the Caliph. | |
| 728 | Death of Hasan al Basri, well known Sufi Shaykh. | |
| 731 | Death of Imam al Baqir. | |
| 732 | Charles Martel stops the Muslim advance into Europe at the Battle of Tours. | |
| 735 | Muslim armies advance through southern France and occupy mountain passes in Switzerland. | |
| 740 | Death of Imam Zaid bin Zain ul Abedin. | |
| 743 | Al Walid II becomes the Caliph. | |
| 744 | Abu Muslim is appointed the chief dayee of Khorasan. | |
| Yazid III, Ibrahim and Marwan II become the Caliphs in rapid succession. | ||
| 745 | Imam Ja’afar as Saadiq discusses Fiqh issues in his study circles. Imam Abu Haneefa participates in these studies and benefits from them. | |
| 746 | Beginning of the Abbasid revolution in Khorasan. | |
| 747 | Kufa falls to the Abbasids. Abu Muslim nominates Abul Abbas as the first Abbasid Caliph. | |
| 750 | The Abbasid Revolution. | |
| The Abbasid forces defeat the Caliph Marwan at the Battle of Kushaf. The Umayyads are swept away from power and are slaughtered. | ||
| Abdur Rahman I escapes to Spain. | ||
| Beginning of the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad. Abu Abbas al Saffah becomes the first Abbasid Caliph. | ||
| 751 | Battle of Tlas. The Muslim armies are victorious over the forces of the Tang Empire. China cedes Central Asia to the Caliphate. | |
| Systematic development of Fiqh begins. | ||
| 754 | Al Mansur becomes the Caliph, sends troops into China in response to a request for help from the Tang Emperor Tsung. | |
| 755 | The Umayyad Abdur Rahman I establishes the Umayyad Emirate in Cordoba, Spain. | |
| 759 | The Franks recapture Narbonne from the Muslims. | |
| 760 | Death of Imam Ismail, son of Imam Ja’afar as Saadiq. | |
| Beginning of the Fatimid branch among Muslims. | ||
| 763 | Baghdad becomes the seat of the Caliphate and the cradle of Islamic civilization. | |
| 765 | Death of Imam Ja’afar as Saadiq, one of the principal sources of Fiqh. Caliph al Mansur establishes schools of translation in Baghdad. | |
| Muslims come into contact with Greek philosophy and Indian mathematics. | ||
| 768 | Death of Imam Abu Haneefa, after whom the Hanafi school of Fiqh is named. | |
| Charlemagne (768-814) ascends the Frankish throne. | ||
| 775 | Al Mahdi becomes the Caliph. | |
| 778 | Charlemagne of France raids Muslim Spain. | |
| 780 | Charlemagne invades German territories and converts the Germans to Christianity. | |
| 781 | Ibn Jabir invents the science of chemistry. | |
| 785 | Al Hadi becomes the Caliph. | |
| 786 | Harun al Rashid becomes the Caliph. Golden age of Baghdad. | |
| 788 | Beginning of the Idrisid dynasty in North Africa. | |
| 790 | The manufacture of paper is introduced into Baghdad from China. | |
| 795 | Death of Imam Malik bin Anas, after whom the Maliki school of Fiqh is named. | |
| 799 | Zubaida, wife of Harun al Rashid performs the Hajj and builds rest houses for hajjis on the road. | |
| Death of Imam Musa al Kazim. | ||
| 800 | Harun al Rashid and Charlemagne exchange ambassadors. | |
| back to top | ||
| 801 | The city of Fez is established. | |
| Charlemagne begins an invasion of Muslim Spain. | ||
| 802 | Death of Rabia al Adawiya, one of the most celebrated spiritual luminaries and a teacher of Sufi masters. | |
| 809 | Death of Harun al Rashid. Al Amin becomes the Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| 813 | Al Mamun succeeds his brother Al Amin as the Caliph. | |
| 814 | Death of Charlemagne. The Carolingian Empire in Europe begins to disintegrate. | |
| 815 | Al Khwarizmi invents the science of Algebra and develops the mathematics of equations. | |
| Viking raids from the North ravage Europe. | ||
| The Abbasid Empire begins a slow process of disintegration. The Idrisids in North Africa and the Tahirids in Persia become autonomous. | ||
| 818 | Death of Imam Ali al Rida. | |
| 820 | Death of Imam al Shafi’i, after whom the Shafi’i school of Fiqh is named. | |
| Rise of the Aghlabids in North Africa. | ||
| 822 | Music flourishes at the court of Cordoba under the musician al Zirhab. | |
| The Aghlabid armies from North Africa invade Sicily. | ||
| 827 | Caliph al Mamun adopts Mu’tazilite doctrines as court dogma. | |
| The Idrisids capture Crete, Sardinia and Sicily. | ||
| 830 | Caliph al Mamun patronizes the Bait ul Hikmah (House of Wisdom) in Baghdad and encourages translation of Greek and Sanskrit books into Arabic. The Muslims develop concept of decimals in mathematics. | |
| 831 | Muslims capture Palermo Italy. | |
| 833 | Death of Al Mamun. Al Mu’tasim becomes the Caliph and enlists Turks into the army. | |
| 835 | Death of Imam al Jawwad. | |
| 838 | Umayyad armies from Spain occupy Marseilles France. | |
| 840 | Death of al Khwarizmi, mathematician, Sufi shaykh. | |
| 842 | Al Wathiq becomes the Caliph. | |
| 846 | The Aghlabids in North Africa occupy Pisa and conduct a raid on Rome. | |
| 847 | Al Mutawakkil becomes the Caliph; abandons Mu’tazilite doctrines. | |
| 850 | Turkish influence in the Caliphate grows. | |
| 855 |
Death of Imam ibn Hanbal, after whom the Hanbali school of Fiqh is named.
|
|
| 861 | University of Kairaouine (established 859 CE) in Fes, Morocco. Caliph al Mutawakkil is murdered in Baghdad. Al Muntasir becomes the Caliph. | |
| 866 | Al Mu’taz becomes the Caliph. | |
| 868 | Egypt becomes autonomous under the Tulunids. | |
| Palermo, in Sicily, becomes a center of Islamic learning. | ||
| Death of Imam al Hadi. | ||
| 870 | The Zanj, workers from East Africa, revolt in Iraq. | |
| Death of Al Farabi and Al Kindi, noted men of science. | ||
| Death of Al Tabari, renowned physician. | ||
| The Muslims capture Malta. | ||
| Al Mu’tamid becomes the Caliph in Baghdad. | ||
| 874 | Death of Abul Hussain Muslim, compiler of Hadith. | |
| Death of Imam al Askari. | ||
| Death of al Kindi, mathematician, astronomer. | ||
| Death of al Bistami, one of the most celebrated Sufi Shaikhs. | ||
| 875 | Hamdan Karamat starts the Karamatian movement. | |
| The Sassanids establish themselves in Bokhara. | ||
| 878 | Disappearance of Imam al Muntazar, the Twelfth Imam. | |
| Beginning of belief in the hidden Imam. | ||
| 880 | The Aghlabids lose southern Italy to Christian forces. | |
| 882 | A rebellion of the Zanj in Iraq is crushed. | |
| 885 | Death of Dawud ibn Khalaf, expounder of the Zahiri school of Fiqh. | |
| 887 | Peasant revolt in China against foreigners forces out the Muslims of Canton. | |
| 889 | Death of ibn Kutaiba, historian. | |
| 890 | Spanish Muslims re-establish bases in southern France and conduct raids into Switzerland. | |
| 892 | Death of Muhammed al Tharmidi, historian. | |
| Al Mu’tadid becomes the Caliph. | ||
| 893 | The Karamatians capture Yemen. | |
| 898 | Imam al Hadi Yahya establishes a Zaidi state in Yemen. | |
| 900 | The Arabian Nights are compiled. | |
| Improvements appear in the design and use of the Astrolabe. | ||
| The Kharijites establish a dynasty in Sijilmasa, North Africa. | ||
| back to top | ||
| 901 | The Samanids emerge in Khorasan, Persia. | |
| 902 | Al Muktafi becomes the Caliph. | |
| 903 | The Karamatians plunder Damascus. | |
| 904 | Muslim armies capture Solonika from the Byzantines. | |
| 907 | Abu Abdullah, Fatimid leader, moves to North Africa. | |
| 908 | Al Muqtadir becomes the Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| 909 | The Fatimids establish themselves in North Africa. | |
| Ubaidulla al Mahdi becomes the first Fatimid Caliph. | ||
| 910 | Al Razi conducts research into infectious diseases including small pox, rabies and the plague. | |
| 912 | Reign of Abdul Rahman III in Spain (912-961). Cordoba becomes the premier city of Europe. Golden age of Spain. Science and civilization thrive. | |
| 914 | Nasr al Saeed of the Samanids in Khorasan favors the Fatimids over the Abbasids. | |
| 915 | The Kharijites establish themselves in southern Morocco. | |
| The Fatimids raid Egypt. | ||
| 922 | Mansur al Hallaj, Persian mystic, is executed for his esoteric views. | |
| Beginning of the Tahirid dynasty in Iraq. | ||
| 923 | Death of Abu Tabari, noted commentator on the Qur’an. | |
| 925 | Death of al Razi, doctor of medicine. | |
| 929 | In response to Fatimid claims to the Caliphate, Abdul Rahman III of Spain assumes the title of Caliph and protector of Sunni Muslims in North Africa. | |
| 930 | The Karamatians raid Mecca and carry off the Hijr e Aswad from the Haram to Bahrain. | |
| 931 | Abdur Rahman III occupies Ceuta. | |
| The Fatimids capture Algeria. | ||
| 932 | The Buyids establish their rule in southern Iraq. | |
| Al Qahir becomes the Caliph in Baghdad. | ||
| 933 | The Ishkedids displace the Tulunids in Egypt and rule until 969. | |
| 934 | Al Radi becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | |
| Al Qaim becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | ||
| 936 | Death of al Ashari (874-936), highly influential theologian who reconciled Mu’tazilite doctrines with orthodox theology. Author of “occasionalism” in philosophy. | |
| 939 | Abdul Rahman III of Spain captures Fraxinetum, Valais, Geneva, Toulon and Great St. Bernard. | |
| 940 | Extensive postal services are established by the Abbasids. | |
| Al Muttaqi becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | ||
| 945 | The Buyids temporarily capture Baghdad. | |
| 946 | Al Mutee’ becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | |
| Al Mansur becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | ||
| 950 | Death of Al Farabi, noted scientist, philosopher, jurist, author of treatises on ethics, music and logic, Sufi Shaykh. | |
| 951 | The Ikhwan as Safa in Iraq compile an Encyclopedia of Knowledge. | |
| 953 | Al Muiz becomes the Fatimid Caliph in North Africa. | |
| 955 | Sharp naval engagements between the navies of Al Muiz and Abdul Rahman III off the coast of Spain. | |
| 957 | Al Masudi, the historian, passes away. | |
| 961 | Death of Abdul Rahman III. | |
| The Oghuz family of Turks in Central Asia accepts Islam. | ||
| 962 | The Seljuk, Alaptagin, establishes a kingdom in Ghazna, Afghanistan. | |
| 968 | The Umayyads establish a university in Cordoba. | |
| 969 | The Fatimids conquer Egypt and establish the city of Cairo. | |
| 970 | The Fatimids capture Syria, Mecca and Madina and lay claim to the leadership of the Islamic world. Fatimid rule in Multan (modern Pakistan). Brisk trade between Alexandria, Egypt and Venice, Italy. | |
| 971 | The Fatimids establish Al Azhar University in Cairo. | |
| 974 | Al Ta’ee becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | |
| 975 | Death of Al Muiz, Fatimid Caliph of Egypt. Al Aziz becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | |
| Muslim astronomers publish manuscripts showing constellations of stars. | ||
| 988 | Count Vladimir of Kiev embraces Eastern Orthodox Christianity. | |
| 991 | Al Qadir becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | |
| 996 | Al Hakim becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | |
| Pope Pious XI declares the Crusades against Muslims. | ||
| 997 | Mahmud succeeds Alaptagin in Ghazna and dominates Central Asia. | |
| 999 | Large scale Turkish migrations into Central Asia. | |
| Kara Khani Turks occupy Bukhara. | ||
| Mahmud of Ghazna annexes Khorasan. | ||
| 1000 | Mahmud makes the first of seventeen raids into India. | |
| The Chinese use gunpowder to propel arrows. | ||
| back to top | ||
| 1001 | Mahmud starts campaigns to capture Peshawar, Bhera, Nagarkot, Tarain, Thaneshwar and Kanauj in India. | |
| 1004 | Mahmud defeats Dawud, Fatimid ruler of Multan. | |
| 1016 | The Christians reclaim Sardinia. | |
| 1017 | Beginning of the Druze sect in Lebanon. | |
| 1020 | Death of Firdowsi of Persia, author of Shah Nama. | |
| Mahmud establishes Lahore as the capital of Punjab. | ||
| Death of Fatimid Caliph al Hakim who had claimed divinity. | ||
| 1021 | Al Zahir becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | |
| 1024 | Mahmud raids temple of Somanath in Gujrat, India. | |
| 1025 | Al Baruni publishes Kitab ul Hind, a penetrating study of the people of India. | |
| 1030 | Death of Mahmud of Ghazna. Umayyad caliphate in Cordoba defeated by the Christian Reconquista. |
|
| 1031 | The Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba disintegrates. Spain breaks up into petty emirates. The Christian kingdoms of Castille, Leon and Portugal position themselves to attack the Muslim territories. | |
| Al Qaim becomes the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | ||
| 1032 | The Church of Constantinople breaks with the Church of Rome over the issue of icons in the Church. | |
| 1036 | Taghril Beg becomes Seljuk Sultan. | |
| Al Mustansir becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | ||
| 1037 | Death of Abu Ali ibn Sina, one of the greatest of physicians. | |
| Ferdinand I, king of Castille, captures Leon. | ||
| 1038 | Death of Al Hazen, noted physicist. | |
| 1043 | The Fatimid Empire begins to crumble. Mecca, Madina, Yemen and North Africa are lost by the Fatimids. | |
| 1048 | Death of al Bairuni, historian, author of Kitab ul Hind. | |
| 1050 | The Christians advance in Sicily. | |
| 1051 | Beginning of the Murabitun revolution in West Africa. | |
| 1056 | The Seljuk Taghril Beg and the Buyid Basisiri contest the control of Baghdad. | |
| 1058 | Taghril Beg is anointed by Abbasid Caliph Kaim as “sultan of the east and the west” for his role in protecting the Abbasid Caliphate. | |
| 1060 | The Seljuk Turks advance into Persia, Azerbaijan and Armenia. | |
| The Crusaders raid the coast of North Africa. | ||
| 1061 | The Murabitun capture Morocco. | |
| The Murabitun establish the city of Marrakesh as their capital. | ||
| 1063 | Taghril Beg dies childless. His nephew Alap Arsalan becomes the Seljuk sultan. | |
| 1068 | Beginning of the Songhay Empire in West Africa. | |
| 1072 | Battle of Manzikert. The Seljuk Turks under Alap Arsalan defeat the Byzantines under Emperor Romanus and open up Anatolia for Turkish settlement. | |
| The Christians capture Palermo in Sicily. | ||
| 1075 | The Seljuk Sultan Malik Shah retakes Syria from the Fatimids. | |
| Al Muqtadi becomes the Abbasid Caliph. | ||
| 1077 | Birth of Abdul Qader Jeelani, celebrated Sufi sage. | |
| 1085 | Alfonso I of Castile captures Toledo, the ancient capital of Visigoth Spain. The extensive libraries of Toledo become accessible to Christian Europe. | |
| 1086 | The Murabitun emir, Yusuf bin Tashfin, advances into Spain at the head of a powerful African force. | |
| The Nizamiya College is founded in Baghdad by Nizam ul Mulk, grand vizier to Sultan Malik Shah. | ||
| 1087 | Yusuf bin Tashfin defeats Alfonso VI at the Battle of Sagrajas. | |
| The Crusaders sack Mahdiya in North Africa. | ||
| The assassin terror grows in Iraq and Syria. | ||
| 1090 | Al Ghazzali teaches at NizamiyaCollege, Baghdad. | |
| The Crusaders capture Malta. | ||
| The assassins capture Alamut in northern Syria and establish a training center for fidayees. | ||
| 1091 | End of Muslim presence in Sicily. | |
| Smyrna in Anatolia becomes the Seljuk capital. | ||
| Death of Sultan Malik Shah. | ||
| The assassins murder grand vizier Nizam ul Mulk. | ||
| 1094 | Al Mustansir becomes the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| Al Mustadi becomes the Fatimid Caliph in Cairo. | ||
| 1095 | Pope Urban II declares a Crusade to take Jerusalem. | |
| Al Afdal, grand vizier of Fatimid Egypt, recaptures Jerusalem from Turkish emir Duqaq of Damascus. | ||
| 1096 | The start of the First Crusade. | |
| 1097 | Konya Anatolia becomes the Seljuk capital. | |
| The Turks retreat before the advancing Crusaders. | ||
| The Fatimids in Egypt start negotiations with the Crusaders to divide up Seljuk territories. | ||
| 1098 | The Crusaders capture Antioch. | |
| 1099 | Jerusalem falls to the Crusaders. The Muslims and the Jews are massacred. Baldwin becomes king of Jerusalem. | |
| 1100 | Al Ghazzali writes a powerful diatribe, Tahaffuz al Falsafa, against speculative philosophy. In Ihya al Uloom, he accords tasawwuf an honored position in the Islamic sciences. | |
| back to top | ||
| 1101 | Shaykh Abdullah Arif introduces Islam into the island of Sumatra, Indonesia. | |
| 1106 | Death of Yusuf bin Tashfin, emir of the Murabitun. | |
| 1111 | Abu Hamid al Ghazzali dies after transforming the intellectual landscape of the Islamic world. | |
| 1113 | Maudud, a Seljuk officer from Mosul, defeats King Baldwin of Jerusalem. | |
| 1118 | Al Mustarshid, Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| 1123 | Death of Omar al Khayyam, mathematician, mystic. | |
| 1124 | Death of Hassan al Sabbah, leader of the Assassins. | |
| 1126 | Archbishop Raymond establishes a school in Toledo to translate Arabic books into Latin. | |
| 1127 | The Assassins murder Turkish officer Maudud. | |
| 1130 | Death of ibn Tumart, leader of the Al Muhaddithin. | |
| 1132 | Roger II of Sicily invites Muslim scholars to work at his court. | |
| 1139 | Birth of Khwaja Moeenuddin Chishti, Sufi sage. | |
| 1141 | The Kara Kitai Turkomans defeat the Seljuks at Amu Darya. | |
| 1144 | The Seljuks, under Zengi, recapture Edessa. | |
| Pope Eugene declares the Second Crusade. | ||
| 1145 | The Second Crusade collapses in Anatolia but succeeds in capturing Lisbon in Portugal. | |
| End of the Murabitun rule in Andalus. | ||
| 1146 | The al Muhaddithin captures Morocco. | |
| The assassins murder Seljuk Emir Zengi. | ||
| 1149 | Al Zafir becomes the Fatimid Caliph. | |
| 1150 | The University of Paris is established. | |
| 1151 | Al Idrisi constructs a map of the then known world. | |
| 1154 | The Kurdish officer Nuruddin, in Seljuk service, takes Damascus. | |
| Al Faiz becomes the Fatimid Caliph in Cairo. | ||
| 1157 | The al Muhaddithin captures Andalus. | |
| 1160 | Al Mustanjid becomes the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| Al Adid, the last of the Fatimids, becomes the Caliph in Cairo. | ||
| 1163 | The Seljuks and the Crusaders compete for influence in Fatimid Egypt. | |
| 1166 | Death of Shaykh Abdul Qader Jeelani of Baghdad, called Shaykh ul Mashaiq, founder of the Qadariya Sufi order. | |
| Death of the geographer, al Idrisi. | ||
| 1167 | Establishment of Oxford University in England. | |
| 1170 | Salahuddin takes Egypt from the Fatimids. | |
| Al Mustadi becomes the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | ||
| 1171 | End of the Fatimid era. Egypt reverts to the Abbasid Caliphate. | |
| 1173 | Ghiasuddin Ghori established the kingdom of Ghor in Afghanistan. | |
| 1175 | Salahuddin consolidates his hold on Syria and Egypt. | |
| Death of Ahmed al Rifai, founder of the Rifaiyah Sufi brotherhood. | ||
| 1177 | Muhammed Ghori adds Multan, Uch, Dera Ismail Khan and Sindh to his dominions. | |
| 1179 | Muhammed Ghori starts campaigns to capture Peshawar and Sialkot. | |
| 1182 | Khwaja Muhammed Ghouse of Sindh introduces the Qadariya order into India and Pakistan. | |
| 1187 | Battle of Hittin. Salahuddin triumphs and recaptures Jerusalem. | |
| Muhammed Ghori captures Lahore. | ||
| 1188 | Pope Clement III launches the Third Crusade. | |
| 1189 | Khwaja Moeenuddin Chisti moves to Ajmer, India and establishes the Chistiya order. | |
| 1190 | King Richard of England proposes a marriage between his sister and Saifuddin, brother of Salahuddin and for the two together to rule Jerusalem. The proposal is opposed by the Crusaders and is abandoned. | |
| 1191 | Accra surrenders to the Crusaders after a long siege. | |
| Mohammed Ghori suffers a defeat at the Battle of Tarain and is forced to withdraw towards Kabul. | ||
| 1192 | Muhammed Ghori, victorious over the Rajputs, captures Delhi. Prithvi Raj Chauhan, ruler of Ajmer and Delhi is slain. | |
| 1193 |
Salahuddin passes away and is buried in Damascus. |
|
| 1196 | The al Muhaddith emir al Mansur defeats the Crusaders at the Battle of Alarcos. | |
| 1198 | Death of ibn Rushd, of the great world philosophers. | |
| 1199 | Pope Innocent III declares the Fourth Crusade. | |
| 1200 | Islam takes roots in Indonesia. | |
| Alauddin Muhammed becomes the Shah of Khwarazm. | ||
| The Crusaders capture Valencia. | ||
| Cambridge University is established in England. | ||
| back to top | ||
| 1201 | The Latin Crusaders sack Zara, a Christian city on the Adriatic. | |
| 1202 | The Delhi Sultanate is established. | |
| 1203 | Death of Nizami, well known Farsi poet. | |
| 1204 | The Crusaders, led by Dondolo of Venice, sack Constantinople and loot its treasures. | |
| Johan Shah, ruler of Sumatra, accepts Islam. | ||
| 1205 | The Turkoman Kara Kitai defeats Mohammed Ghori. | |
| The Ghorids put down a rebellion in the Punjab. | ||
| 1206 | Genghiz Khan becomes the supreme ruler of the Mongol tribes. | |
| The assassins murder Muhammed Ghori. | ||
| The Delhi sultans advance towards Bengal. | ||
| 1211 | Altumish ascends the throne of Delhi. | |
| 1212 | The Crusaders defeat the al Muhaddith at the Battle of Las Novas de Tolosa. | |
| 1215 | Genghiz Khan captures northern China; learns the use of gunpowder from the Chinese. | |
| 1218 | The Fifth Crusade is directed against Egypt. The Egyptians open the Nile docks and drown the invaders. | |
| 1219 | Genghiz Khan invades the territories of Shah Muhammed of Khorasan. | |
| 1220 | Genghiz Khan devastates Central Asia. | |
| 1221 | Genghiz Khan destroys Persia and Afghanistan. | |
| Prince Jalaluddin faces the Khan at the Battle of the Indus. | ||
| 1222 | Genghiz Khan returns to Mongolia. | |
| 1223 | Ibn al Athir, celebrated historian, passes away. | |
| 1227 | Death of Genghiz Khan. The Mongols continue their advance through West Asia and Eastern Europe. | |
| 1228 | The Sixth Crusade, directed at Egypt and led by Emperor Frederick II of Germany fails. | |
| 1230 | Sundiata starts consolidation of the Empire of Mali. | |
| 1235 | Baba Fareed of Lahore becomes heads of the Chistiya order in India. | |
| 1236 | Cordoba, capital of Muslim Spain, falls to the Crusaders. | |
| Razia rules as Queen of India. | ||
| Death of Khwaja Moeenuddin Chishti of Ajmer, the most celebrated awliya of the subcontinent. | ||
| Al Mustansir becomes the Caliph in Baghdad. | ||
| 1240 | Death of ibn al Arabi, renowned Sufi Shaykh. | |
| Roger Bacon teaches in England. | ||
| 1242 | Al Musta’sim becomes the 37th and the last Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad. | |
| 1245 | At the Council of Lyons, Christian Europe resolves to seek an alliance with the Mongols against the Muslims. A Franciscan priest, John de Plano Carpini, arrives at the Mongol court to seek military assistance. | |
| 1248 | Seville in Spain falls to the Christians. | |
| Ibn Ahmar starts the Nasirid dynasty in Granada. | ||
| 1249 | The Seventh Crusade, directed at Egypt by the Franks, is beaten back. | |
| 1250 | Shajarat al Durr rules as Queen of Egypt. | |
| 1251 | Hulagu Khan becomes the Mongol lord of Persia and Central Asia. | |
| 1256 | Hulagu Khan destroys the Assassins. | |
| 1257 | Death of Shaykh Saadi, celebrated Farsi poet. | |
| Nizamuddin Awliya becomes head of the Chishtiya order in Delhi. Islam spreads in India. | ||
| 1258 | Hulagu Khan sacks Baghdad. End of the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad. The curtain falls on the classic Islamic civilization. Caliph al Musta’sim is killed. | |
| Death of Ali al Shadhuli, founder of the Shadhuli Sufi order. | ||
| 1260 | Kublai Khan ascends the throne of China. Many capable Muslims work at the court of the Great Khan. | |
| Hulagu Khan storms Aleppo and massacres its inhabitants. | ||
| 1261 | The Mamlukes of Egypt install Al Mustansir as the Abbasid Caliph in Cairo. | |
| The Mamluke, Zahir Baybars of Egypt, defeats a combined army of Mongols, Armenians and Crusaders at the Battle of Ayn Jalut. | ||
| 1265 | Death of Hulagu Khan. | |
| 1269 | The Merinide al Yakub captures Marrakesh. | |
| 1273 | Death of Jalaluddin Rumi, author of Mathnavi, the most celebrated of Farsi poets and founder of the Maulavi Sufi order. | |
| 1274 | Death of al Tusi, astronomer and inventor of the 2-axis gimbal. | |
| Emir al Yaqub of the Merinides defeats the Christians at the Battle of Ecija. | ||
| 1277 | Sultan Baybars defeats the Mongol armies at the Battle of Abulistan. | |
| 1278 | Death of Sultan Baybars. | |
| 1289 | The Mamlukes captures Acre, last Crusader stronghold in Syria. | |
| 1290 | Sultan Malik Shah rules in Sumatra. | |
| 1291 | Death of Shaykh Saadi, well known Farsi poet. | |
| 1294 | Marco Polo returns to Italy from journey to the East. | |
| 1295 | Ghazan the Great, the Il Khan Emperor, accepts Islam. | |
| 1300 | Alauddin Khilji consolidates his empire over the subcontinent. Malik Kafur advances into southern India. | |
| back to top | ||
| 1301 | Uthman Ghazi, founder of the Ottoman Empire, consolidates his holdings around Burs and Eskishehir; he defeats the Byzantines at the Battle of Yalakova. | |
| The Mamlukes triumph over the Il Khans at the Battle of Marj as Suffar. | ||
| 1307 | Mansa Musa becomes emperor of Mali. | |
| 1316 | Death of Alauddin Khilji, emperor of India. | |
| 1320 | The Khilji dynasty in India collapses. | |
| Beginning of the Tughlaq dynasty. | ||
| 1324 | Mansa Musa performs his hajj with an entourage of 12000. | |
| 1325 | Death of Nizamuddin Awliya of Delhi. | |
| Ibn Batuta begins his journey around the world. | ||
| Death of Amir Khusroe, famed Sufi poet of India. | ||
| 1326 | Death of Uthman I, founder of the Ottoman Empire. His successor Sultan Orkhan captures Bursa. | |
| Death of ibn Taymiyah, noted scholar, considered to be the founder of the “salafi” school of thought. | ||
| 1333 | Yusuf I becomes emir of Granada, breaks with Castille, forms an alliance with the sultan of Morocco and makes a last attempt to capture Spain from the Christians. | |
| 1334 | Ibn Batuta arrives in Delhi. | |
| Death of Shaykh Safiuddin Ishaq, after whom the Safavid dynasty of Persia is named. | ||
| 1335 | Death of Abu Said, Il Khanid Prince. | |
| 1340 | The Yuan Emperor Toghon Timur of China sends an embassy to the court of Muhammed bin Tughlaq of India. | |
| The Merinide navy defeats the Spaniards at the Battle of Tarifa. | ||
| 1341 | Death of Sultan ibn Qalawun of Egypt. | |
| 1345 | Ibn Batuta visits Sultan Malik al Zahir of Pasai Indonesia. | |
| 1346 | The Black Plague devastates Europe. | |
| 1351 | Death of Muhammed bin Tughlaq of India. The Tughlaq Empire begins to disintegrate. | |
| 1354 | Ibn Batuta visits the Empire of Mali. | |
| The Ottomans capture Gallipoli and Ankara. | ||
| 1355 | Ibn Batuta returns to Tangier. The Merinide Sultan Abu Inan authorizes the writing of the Rehla of Ibn Batuta. | |
| The Genoese briefly occupy Tripoli, Libya. | ||
| 1357 | The Ottomans capture Erdirne. | |
| 1368 | Timurlane, elected the leader of the Tatars, consolidates his hold on the valley of Farghana in Uzbekistan. | |
| 1369 | Death of ibn Batuta. | |
| 1375 | Dimitrius, Count of Moscow, wins a victory over the Tatar Golden Horde. | |
| 1376 | The Golden Horde burns down Moscow. | |
| 1380 | Timurlane begins his first campaign in Persia. | |
| Shaykh Awliya Karim al Maqdum introduces Islam into Mindanao, the Philippines. | ||
| Kara Muhammed, leader of the Turkish tribe Kara Kuyunlu, establishes his kingdom near Mosul. | ||
| 1381 | The Ottomans capture Bulgaria. | |
| 1385 | The Ottomans capture Thrace. | |
| 1387 | Timurlane invades Russia and destroys the power of the Golden Horde. Russia begins its long march towards political consolidation. | |
| 1389 | Bayazid I becomes the Ottoman sultan, defeats the Serbs at the Battle of Kosova. | |
| Death of Hafiz, one of the greatest of Farsi poets. | ||
| Death of Bahauddin Naqshband, founder of the Naqshbandi Sufi tareeqa of Bukhara. | ||
| 1390 | A combined French and Genoese force attacks Mahdiya, Tunisia. | |
| 1391 | Bayazid I attacks Constantinople. | |
| 1396 | Bayazid defeats the Crusader armies at the Battle of Nicopolis. | |
| 1398 | Timur sacks Isfahan, Persia. | |
| 1399 | Timur invades India, sacks Delhi, India. | |
| Castille sacks Tetuan, Morocco. | ||
| 1400 | Bayazid I lays siege to Constantinople. | |
| back to top | ||
| 1401 | Timur defeats the Mamlukes of Egypt. | |
| Damascus surrenders to the Tatars. | ||
| Timur sacks Baghdad. | ||
| 1402 | Timur defeats Bayazid I at the Battle of Ankara. | |
| Sulaiman I becomes the Ottoman sultan. | ||
| Sultan Iskander Shah expels the Thais from Malaya. | ||
| 1404 | Timur embarks on an expedition to China. | |
| 1405 | Timurlane dies en route to China; his son Shah Rukh succeeds him. | |
| 1406 | Sultan Sikander Shah of Malaysia accepts Islam. | |
| The great Chinese Admiral Zheng Yi (commonly known as Admiral Ho), a Muslim, sails to Malaya, Indonesia, India, Persia, Yemen, East Africa and the Cape of Good Hope with a fleet of 50 great ships. | ||
| Death of ibn Khaldun, author of Muqaddamah. | ||
| 1409 | Shah Rukh, heir to Timurlane, occupies Samarqand. | |
| 1410 | Kara Yusuf establishes the Kara Kuyunlu kingdom around Tabriz, Persia. | |
| Death of Gaysu Daraz, Sufi shaykh of the Deccan, India. | ||
| 1411 | Sultan Iskander Shah of Malaya visits China at the invitation of the Chinese Emperor. | |
| Prince Mehmet begins the reconsolidation of the Ottoman Empire after the disastrous defeat in the Battle of Ankara. | ||
| 1415 | The Portuguese capture Ceuta in Morocco. | |
| 1420 | Shah Rukh consolidates his hold on Persia. | |
| 1421 | Murad II becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| 1422 | Murad II lays unsuccessful siege to Constantinople. | |
| 1424 | Death of Sultan Iskander Shah of Malaya. | |
| 1425 | Tangier in Morocco, captured by the Portuguese. | |
| 1430 | The Portuguese acquire the technology to sail against the wind from the Venetians. | |
| 1432 | Portuguese captain Diaz sails around Cape Bajador in West Africa. | |
| 1434 | Death of Shah Rukh. Persia disintegrates. The Kara Kuyunlu and Aq Kuyunlu expand their territories. | |
| Ulugh Bey of Farghana (Uzbekistan) authorizes the construction of an observatory in Samarqand. | ||
| 1441 | First slave raid by the Portuguese in southern Morocco directed against Muslims. | |
| 1443 | The Portuguese capture the island of Tristao off the coast of West Africa, later to gain notoriety in the Atlantic slave trade. | |
| 1444 | Ottomans armies march into Hungary. | |
| Murad II defeats combined armies of Hungary, Wallachia and Venice at the Battle of Varna. | ||
| The Portuguese Lagos Company chartered under Prince Henry. | ||
| 1445 | Printing is introduced into Europe. Portuguese sailor Diaz sails around West Africa. | |
| 1451 | Mehmet II becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| Shaykh Rahmat converts the Majapahit ruler (Indonesia) Raja Kertawijaya to Islam. | ||
| Islam spreads rapidly in Java. | ||
| 1453 | Mehmet II conquerors Constantinople, renames it Istanbul and makes it the capital of the Ottoman Empire. | |
| 1455 | The Venetians sail to the delta of the Gambia River. | |
| 1456 | Mehmet II captures Athens, Greece. | |
| The Portuguese arrive at the mouth of the Gambia River. | ||
| 1458 | The Portuguese occupy the fortress of al Qasr, Morocco. | |
| 1460 | King Alfonso of Portugal authorizes Fernao Gomes to explore the western coast of Africa. | |
| 1461 | Leonardo da Vinci begins his work in Venice. | |
| 1463 | Mehmet II conquers Bosnia. Mosque of Sultan Mehmet II constructed in Istanbul. | |
| 1465 | Death of al Jazuli, Sufi Shaykh in Morocco. | |
| 1467 | Herzegovina conquered by Mehmet II. | |
| Uzun Hassan, leader of Aq Quyunlu defeats Jehan Shah, leader of the Kara Quyunlu. Jehan Shah dies in battle. | ||
| 1471 | Tangiers occupied by Portugal. | |
| Portugal occupies Arzila on the West coast of Morocco. | ||
| 1473 | Ottoman Sultan Mehmet II defeats the Aq Kuyunlu Sultan Uzun Hassan. Portuguese captain Sequira sails to Benin, Nigeria. | |
| 1474 | Commercial town of Kedah, in Indonesia, becomes Muslim. | |
| 1475 | War between Spain and Portugal over rights to the Canary Islands. | |
| 1478 | Kara Quli, a descendant of Jehan Shah, flees to India and establishes the Qutubshahi dynasty near Hyderabad. | |
| Death of Uzun Hassan, Aq Quyunlu Sultan. | ||
| Turmoil in western Persia. | ||
| 1479 | Consolidation of Spain under Ferdinand and Isabella. | |
| 1480 | The Ottomans capture the island of Rhodes. | |
| 1481 | Bayazid II becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| 1482 | Ferdinand of Spain attacks al Hama. | |
| 1483 | Civil wars in Granada. | |
| Ferdinand captures Malaga, Spain. | ||
| 1484 | The Portuguese appear at the delta of the Congo River. | |
| 1487 | Portuguese sailor Diaz rounds the Cape of Good Hope. | |
| 1488 | Malaga, one of the last Nasirid strongholds, falls to Castille. | |
| 1489 | Adil Shah becomes Sultan of Bijapur, India | |
| 1490 | Ferdinand lays siege to Granada, called Santa Fe (Holy Faith). | |
| 1492 | Columbus discovers America. | |
| Granada falls to the Christians. | ||
| Beginning of the Spanish Inquisition. | ||
| The Jews are expelled from Spain. | ||
| Sultan Bayazid II takes Hungary. | ||
| Lodhi Sultanate established in Delhi. | ||
| Death of Abdur Rahman Jami, well known Farsi poet. | ||
| 1493 | Abu Abdallah, commonly known as Boabdil, last emir of Granada, leaves Spain. | |
| Askiya Muhammed becomes Emperor of Songhay. | ||
| 1494 | At the Treaty of Tordesillas arranged by Pope Alexander VI, Portugal and Spain agree to divide up the world for conquest. | |
| 1495 | Shaykh Putah introduces Islam into the Celebes islands and western New Guinea. | |
| 1496 | Vasco da Gama, sails around the Cape of Good Hope and with the help of Muslim navigator Ahmed ibn Majid, discovers route to Malabar, India. | |
| 1497 | Zahiruddin Babur loses Samarqand. | |
| Askiya Muhammed moves the capital of Songhay to Gao on the Niger River. | ||
| 1499 | Ottoman navy defeats the Venetians, takes Lepanto, off the coast of Greece. | |
| 1500 | Muslims in Granada resist the Spanish Inquisition. | |
| Spain institutes forced slavery in Cuba. | ||
| 1501 | Shah Ismail I, with the help of the Safaviyya Sufi order, establishes the Safavid dynasty in Persia. | |
| The Uzbek Shaibani Khan evicts Zahiruddin Babur from Samarqand. | ||
| 1502 | Second voyage of Vasco da Gama to the Indian Ocean. The Portuguese bombard the city-states of East Africa, destroy the port city of Cochin, India and force the Raja of Cochin to expel Muslim traders. | |
| The Portuguese capture Shofala, East Africa. | ||
| Leonardo da Vinci paints the Mona Lisa. | ||
| Inquisition against the Muslims in Spain. | ||
| 1504 | Babur takes Kabul, Afghanistan. | |
| Death of al Maghili, influential thinker from North Africa. | ||
| 1505 | Spain occupies Mars al Kabir, Algeria. | |
| The Portuguese occupy Agadir Morocco and build the fort of Santa Cruz. | ||
| Portuguese captain Almeida raids Kilwa, Tanzania. | ||
| 1507 | The Portuguese occupy Safi, Morocco. | |
| The Portuguese occupy Bab el Mandap at the entrance to the Red Sea. | ||
| 1508 | A Mamluke fleet defeats the Portuguese off the coast of Chaul near modern Karachi. | |
| Spain occupies Oran, Algeria. | ||
| 1509 | The Mamlukes defeat the Portuguese navy off the coast of Yemen. | |
| Shah Ismail I defeats the Uzbek Shaibani Khan at the Battle of Merv. | ||
| Spain occupies Bogie, Tunisia. | ||
| The first batch of slaves bought in Lisbon for transportation to America. | ||
| 1511 | The Portuguese take Goa, India, and make it the capital of their operations in the Indian Ocean. | |
| The Inquisition is instituted against Hindus and Muslim in India. | ||
| Spain destroys Tripoli, Libya. | ||
| The Ottomans crush a Qazilbash uprising in eastern Anatolia at the Battle of Sivas. | ||
| 1512 | Selim I becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| The Portuguese capture the Straits of Malacca. | ||
| Tlemcen in North Africa becomes a protectorate of Spain. | ||
| The Uzbeks defeat the Safavids at the Battle of Khuzduvan and take Khorasan. | ||
| 1514 | Ottoman Sultan Selim I defeats Shah Ismail I at the Battle of Chaldiran. | |
| 1515 | The Portuguese capture the Straits of Hormuz in Persia. | |
| The Portuguese control the entire Atlantic coastline of Morocco. | ||
| First shipload of sugar from Cuba arrives in Spain. | ||
| 1516 | The Portuguese occupy Bahrain and Oman. | |
| The Ottomans capture Mosul. | ||
| Ottoman Sultan Selim I defeats the Mamlukes at the Battle of Marj Dabik in Syria. | ||
| 1517 | Selim I occupies Cairo. | |
| Egypt becomes a province of the Ottoman Empire. | ||
| The Caliphate moves to Istanbul. | ||
| Selim I becomes the first Ottoman Caliph of Islam. | ||
| Muhammed al Mahdi becomes Sa’adid Sultan of Morocco. | ||
| Martin Luther begins Protestant reformation in Germany. | ||
| The Portuguese capture Colombo, Sri Lanka. | ||
| The King of Spain grants license to import African slaves into America. | ||
| Ibrahim Lodhi becomes Sultan of Delhi. | ||
| 1519 | Death of Leonardo da Vinci. | |
| Mexican silver flows into Europe. | ||
| 1520 | Sulaiman the Magnificent becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| 1521 | Sulaiman captures Belgrade. | |
| Cortez destroys the Aztec Empire of Mexico. | ||
| 1522 | Sulaiman captures Rhodes. Spain captures Central America. | |
| 1525 | Death of Safavid Shah Ismail I. | |
| Tahmasp I becomes Safavid ruler of Persia. | ||
| Babur takes Lahore, Pakistan. | ||
| Sulaiman the Magnificent orders a reorganization of the Ottoman fleet to challenge the Spaniards and the Portuguese. | ||
| 1526 | Babur captures Delhi; the Moghul dynasty is born. Sulaiman the Magnificent defeats the Hungarians at the Battle of Mohacs. | |
| 1527 | Babur defeats Rajput armies at the Battle of Khanua. | |
| 1528 | Sultan Sulaiman captures the city of Buda in Hungary. | |
| Askiya Muhammed becomes blind and is deposed as the Emperor of Songhay. | ||
| 1529 | Sultan Sulaiman lays siege to Vienna, Austria. | |
| 1530 | Death of Zahiruddin Babur. His son Humayun ascends the Moghul throne in Delhi. | |
| The Englishman William Hawkins raids the Ivory Coast. | ||
| 1534 | Khairuddin, admiral of the Ottoman fleets, recaptures Tunis. | |
| Henry VIII takes the Church of England out of the orbit of Rome. | ||
| 1535 | Sulaiman Pasha, Ottoman governor of Egypt, drives the Portuguese from Yemen. | |
| The English Parliament passes laws against loitering in London. | ||
| John Calvin preaches the Protestant Reformation in Switzerland. | ||
| Stock Exchange is established in London. | ||
| 1536 | Khairuddin raids Valencia, Spain. | |
| 1537 | Khairuddin captures Otranto, Italy and threatens Rome. | |
| 1538 | Khairuddin victorious over combined navies of Venice and the Vatican at the Battle of Prevesa. | |
| 1540 | Spain colonizes the Philippines. | |
| Destruction of religious relics in England. Beginning of the end of feudalism in England. | ||
| Sher Shah Suri defeats Moghul Emperor Humayun and displaces him from the throne of Delhi until 1555. | ||
| 1541 | Charles V of Spain strikes at the Algerian coast. | |
| Ottoman Admiral Khairuddin takes Otranto, Italy. | ||
| Muhammed al Saadi drives the Portuguese from the fort of Santa Cruz in Morocco. | ||
| 1542 | Increasing tribal warfare in West Africa. | |
| 1546 | Death of Khairuddin. Piri Rais becomes admiral of Ottoman navies. | |
| 1550 | Kingdom of Acheh in Indonesia is founded. Islam spreads in the Archipelago. | |
| 1551 | The Ottomans reclaim Tripoli. | |
| Piri Rais challenges the Portuguese blockage of the Straits of Hormuz. | ||
| 1553 | Thomas Wyndham of England raids the coast of West Africa. | |
| 1554 | John Lock of England raids the Ivory Coast. | |
| 1557 | The Ottomans occupy Masawa, Eritrea. | |
| 1558 | Akbar becomes Moghul Emperor of India. | |
| 1560 | Akbar adds Malwa, Chitoor, Rathambur, Gujrat and Bengal to the Moghul Empire (1560-1574). | |
| Abul Fazal and Faizi, well known writers, grace the Moghul court. | ||
| Akbar surrounds himself with the “seven gems”; men of outstanding capabilities, including the musician Tan Sen and the Finance Minister Raja Todar Mal. | ||
| 1561 | Piri Rais prepares an accurate map of the Atlantic seaboard. | |
| The Ottomans destroy a Spanish fleet at the Battle of Djerba. | ||
| 1562 | Akbar marries Jodha Bai, princess of Amber, Rajasthan. | |
| 1563 | First English fortifications off the coasts of New Guinea. | |
| 1564 | Spain occupies the Philippines. | |
| 1565 | Battle of Telekote, India. The combined forces of Bijapur, Golkunda, Bidar and Gulbarga defeat the armies of Vijayanagar in southern India. | |
| Piri Rais undertakes unsuccessful siege of Malta. | ||
| Akbar, the Great Moghul, captures Gujrat. | ||
| John Hawkins of England conducts slave raids on Sierra Leone. | ||
| Sulaiman the Magnificent passes away | ||
| 1566 | Muslims in Spain rebel against forced conversion to Catholicism. | |
| 1571 | Battle of Lepanto. Combined navies of Spain, Venice, Austria and the Vatican defeat the Ottoman navy and occupy Tunis. Ottoman naval advance into the western Mediterranean is halted. | |
| 1572 | The Ottomans reclaim Tunis. | |
| The Dutch gain their independence from Spain. | ||
| 1573 | The Moghul Emperor Akbar authorizes the construction of four large temples in Mathura. | |
| 1576 | The Ottomans advance through Algeria and take the city of Fez in Morocco. | |
| 1578 | Battle of Al Qasr al Kabir. The Sa’adid Sultan Ahmed al Mansur crushes the Portuguese army. King Sebastian of Portugal is killed. Morocco remains independent. Ottoman westward advance is halted. | |
| 1579 | Akbar, the Great Moghul, completes the construction of a new city, Fatehpur Sikri. He starts ecumenical discussions with all religious faiths in the Ibadat Khana. | |
| 1580 | Ottoman Admiral Ali Beg raids Portuguese positions in East Africa. | |
| Skirmishes between the Empire of Songhay and the Sa’adids of Morocco over the salt mines of Taodini. | ||
| Portugal becomes a protectorate of Spain. | ||
| 1581 | Akbar, the Great Moghul, moves to Lahore, and adds Kashmir, Sindh, Baluchistan and southern Afghanistan to his empire. | |
| Akbar completes the construction of a Jami Masjid in Peshawar. | ||
| Queen Elizabeth I sends Harborne as ambassador to Istanbul to seek trade relations with the Ottomans. | ||
| 1585 | War between the Safavids and the Ottomans for control of Iraq and Azerbaijan. | |
| 1587 | Pope Sixtus V authorizes a Catholic crusade against England. | |
| The English defeat the Scots. Consolidation of Britain under the English throne. | ||
| 1588 | Shah Abbas becomes Safavid emperor of Persia. | |
| The Spanish armada is destroyed off the coast of England. | ||
| Death of Sinan, architect of Sulaimaniye and Shehzade mosques in Turkey. | ||
| 1590 | William Shakespeare writes in England. | |
| 1591 | The Bohras emerge as a sub-branch of the Fatimids. | |
| 1592 | The Sa’adids of Morocco invade the Songhay Empire. A strong force under Judar Pasha destroys Timbaktu. | |
| 1596 | Akbar captures Ahmednagar in the Deccan, India. | |
| 1598 | A second Spanish attempt to conquer England ends in failure. | |
| 1600 | Dutch ascendancy in the Atlantic. The Atlantic slave trade gathers momentum. | |
| The British East India Company is granted a charter by Queen Elizabeth I. | ||
| 1602 | Shah Abbas drives the Portuguese from Bahrain. | |
| The Dutch East India Company is formed. | ||
| 1603 | Death of Queen Elizabeth I. | |
| 1605 | Death of Moghul Emperor Akbar. | |
| 1609 | Final expulsion of Muslims from Spain. | |
| 1615 | The Dutch capture the Straits of Malacca from the Portuguese. | |
| Thomas Roe arrives in India as British ambassador to the Moghul court. | ||
| Galileo is tried by the Church for his view that the earth is not the center of the universe. | ||
| 1619 | The Dutch East India Company obtains trading rights on the island of Java. | |
| Thomas Roe obtains a farman from the Great Moghul Jehangir granting Britain trading rights in India. | ||
| 1620 | Sufi doctrines spread to East Asia. | |
| The Pilgrims land at Port Plymouth, Massachusetts. | ||
| 1622 | Shah Abbas I, with the help of the British navy, expels the Portuguese from the Straits of Hormuz. The British obtain trading rights in Persia. | |
| 1623 | Murad IV becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| 1624 | Death of Shaykh Ahmed Sirhindi, referred to as Mujaddid alf e Thani (Reformer of the Second Millennium). He expounded the doctrine of Wahdat as Shahada. | |
| 1626 | The Dutch establish themselves in New Amsterdam (New York). | |
| 1627 | Shah Jehan, Moghul Emperor of India. | |
| 1630 | Death of German Astronomer Johann Kepler. | |
| 1635 | Death of Mian Pir of Lahore, teacher of Dara Shikoh, son of Shah Jehan. | |
| Emperor Shah Jehan expels the Portuguese from Bengal. | ||
| 1638 | Shah Jehan builds a new capital at Delhi. Construction of the Jami Masjid in Delhi. | |
| 1638 | The British East India Company establishes a factory at Madras. | |
| 1640 | Armed rivalry between Britain, France and the Dutch for control of the slave trade. | |
| Portugal gains its independence from Spain. | ||
| The Dutch capture Sri Lanka. | ||
| The British East India Company establishes a factory at Calcutta. | ||
| 1641 | Sultana Tajul Alam Safiyyiatuddin rules as Queen of Acheh. She is the first of four queens to rule over the northern part of Sumatra. | |
| The Dutch capture Cochin on the West coast of India. | ||
| 1642 | The Dutch establish a colony at Masulipatam on the East coast of India. | |
| 1643 | War between Venice and the Ottomans for control of Crete. | |
| 1648 | Shah Jehan completes the Taj Mahal, the most celebrated monument to love, for his wife Mumtaz Mahal. | |
| The Portuguese recapture Brazil from the Dutch. | ||
| 1655 | The Kurpulu brothers Mehmet Pasha and Fazil Ahmed revitalize the Ottoman administration (1655-1676). | |
| 1658 | Aurangzeb becomes the Moghul Emperor. | |
| 1659 | End of the Sa’adid dynasty in Morocco. | |
| 1660 | Isaac Newton revolutionizes physics. | |
| 1664 | The British seize New Amsterdam, rename it New York. | |
| The Battle of St. Gotthard between the Ottomans and the European “Holy League” ends in a stalemate. | ||
| 1666 | The Qur’an is translated into the Malay language. | |
| 1668 | King Charles II of England sells Bombay to the East India Company. | |
| 1676 | Kara Mustafa Pasha becomes grand vizier in Istanbul. | |
| 1677 | War between Russia and the Ottomans over access to the Black Sea. | |
| 1683 | The second siege of Vienna ends in failure. The Ottomans lose Hungary. | |
| 1686 | The Hapsburgs advance through Hungary towards Belgrade. | |
| The British make an attempt to capture the port of Chittagong in India and are beaten back by Moghul forces. | ||
| 1687 | The Ottomans are defeated at the second Battle of Mohacs. | |
| 1694 | The Bank of England advances a perpetual loan of 1.2 million pounds to the British Crown in return for the privilege of putting its own notes into circulation. | |
| 1696 | Peter of Russia captures the strategic fortress of Azov from the Ottomans. | |
| The Sultan of Oman recaptures Fort Jesus of Mombasa from the Portuguese. | ||
| 1707 | Death of Aurangzeb. The Moghul Empire begins to disintegrate. | |
| 1708 | The assassination of Guru Gobind Singh sets off Sikh revolts against Moghul rule in India. | |
| 1713 | The British displace the Dutch as the most powerful force in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. | |
| 1722 | Tahmasp II, last Safavid ruler of Persia ascends the Persian throne. | |
| Nizam ul Mulk is appointed the Subedar of Hyderabad. | ||
| 1736 | Nadir Shah becomes Emperor of Persia, displaces the Safavid Tahmasp II. | |
| 1739 | Nadir Shah of Persia invades India, sacks Delhi, and carries off the Peacock Throne. | |
| 1740 | Shaykh ibn Abdul Wahhab starts his movement in Najd, Arabia. | |
| 1741 | Ahmed ibn Said becomes Sultan of Oman and Zanzibar and attempts to build a strong navy. | |
| 1746 | Muhammed ibn Saud establishes the Saudi dynasty near Riyadh. | |
| 1754 | The French General Dupleix leaves India. France loses the contest for control of Indian trade to the British. | |
| 1756 | Anglo-French wars in India and America (1756-63). The British are victorious over the French. | |
| 1757 | The Battle of Plassey. The British gain control of Bengal, India. | |
| 1758 | The Industrial Revolution in England gains momentum, fueled by the loot from Bengal. | |
| The Marathas occupy Lahore; oust Timur, son of Nadir Shah of Kabul. | ||
| 1761 | Third Battle of Panipat near Delhi. The Afghans under Ahmed Shah Abdali defeat Maratha armies. | |
| 1762 | Death of Shah Waliullah of Delhi, leading reformer. | |
| 1763 | The Treaty of Paris. The French give up their interests in India and America. | |
| 1764 | The British starve the Begums of Oudh, India, to surrender their jewels. | |
| Battle of Buxor. The British defeat the combined armies of Oudh, Bengal and Delhi. | ||
| 1765 | The British wage a brutal campaign against the Afghans of Rohilla in India. | |
| 1767 | The First Mysore War (1767-68). Tippu Sultan and his father Hyder Ali force the British to sue for peace. | |
| 1772 | The British Parliament abolishes the slave trade. | |
| 1776 | The Colonies declare independence in America. The American War of Independence (1776-83) follows. | |
| 1780 | The Second Mysore War. Tippu Sultan defeats the British at the Battle of Pollipur. | |
| 1781 | George Washington defeats General Cornwallis at the Battle of Saratoga. Cornwallis surrenders at Yorktown, retires to England, is hired by the East India Company, and is sent to battle Tippu Sultan of Mysore. | |
| 1787 | Death of Shaykh ibn Abdul Wahhab of Arabia. | |
| 1789 | The Third Mysore War (1789-91). Cornwallis forces Tippu Sultan to cede half of his Territory; takes Tippu’s children as hostage. | |
| Beginning of the French Revolution. | ||
| 1793 | The British Permanent Settlement Act imposes feudal landlords upon Bengal. | |
| 1798 | Napoleon lands in Egypt and is victorious at the Battle of the Pyramids. | |
| The British capture Colombo from the Dutch. | ||
| 1799 | Napoleon corresponds with Tippu Sultan of Mysore and the Sultan of Oman about an invasion of India. | |
| Tippu Sultan falls at the Battle of Srirangapatam. | ||
| Napoleon is defeated by Nelson at the Battle of Trafalgar and is forced to withdraw from Egypt. | ||
| 1801 | The Wahhabis raid Karbala. Wahhabi movement spreads to Iraq. The Wahhabis raid the Hejaz. | |
| 1803 | Muhammed Ali becomes the Ottoman governor of Egypt; starts a long series of reforms. | |
| The Marathas in Poona, India, sue for peace with the British. | ||
| Denmark abolishes the slave trade. | ||
| Emir Abdul Aziz of Najd captures Mecca. | ||
| 1805 | Muhammed Ali becomes the Pasha of Egypt. | |
| 1806 | British armies enter Delhi. | |
| 1807 | Uthman dan Fuduye establishes the Sokoto Caliphate. | |
| Muhammed Ali Pasha beats back a British attempt to seize Alexandria, Egypt. | ||
| 1808 | The United States abolishes the slave trade. | |
| 1812 | Muhammed Ali of Egypt recaptures Mecca and Hejaz from the Wahhabis (1812-15). | |
| 1817 | Death of Uthman dan Fuduye, mujahid in West Africa. | |
| Muhammed Bello becomes Caliph of the Sokoto Empire. | ||
| 1818 | Holland abolishes the slave trade. | |
| 1821 | Greek war against the Ottomans. | |
| 1827 | Naval Battle of Navarino pits European axis against the Ottomans. | |
| Shaykh Ahmed Lobo establishes the kingdom of Lobo in West Africa. | ||
| 1828 | War between Russia and the Ottomans over control of the Black Sea. Russia advances into Anatolia. | |
| 1830 | Greece breaks off from the Ottoman Empire. | |
| France occupies Algiers. | ||
| 1834 | Beginning of Muslim resistance to the Russians in Daghestan, Crimea and the Caucasus. | |
| 1835 | The Ottomans defeat the French at Malta. | |
| The British replace Persian with English in the higher courts in India. | ||
| 1837 | Sanusiya Sufi brotherhood is founded in North Africa. | |
| 1838 | British invasion of Afghanistan ends in failure. | |
| 1839 | Abdul Mecit I becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| Beginning of Tanzimat reforms in the Ottoman Empire. | ||
| 1840 | France starts colonization of Algeria. | |
| 1846 | The Bank Act of 1846 in England confers legal recognition on the negotiability of credit documents. | |
| 1848 | Nasiruddin Shah ascends the throne of Persia. | |
| 1850 | The Bahai schism starts in Persia. | |
| 1851 | The British build a railroad linking Alexandria with Suez (1851-54). | |
| 1853 | The Tijaniya Sufi brotherhood is established in West Africa. | |
| Beginning of the Crimean War. Britain and France support the Ottomans against Russia. | ||
| 1854 | Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt grants a concession to French Engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps to build the Suez Canal. Egypt borrows funds from international bankers to complete the canal. | |
| The Ottomans take their first loan from international bankers. | ||
| 1856 | End of the Crimean war between Russia and the Ottomans. | |
| 1857 | The Sepoy Uprising in India. After initial successes, the Uprising is crushed by the British. End of Moghul rule. The British exile the last Moghul Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar to Rangoon, Burma. | |
| 1858 | The Russians capture Imam Shamil, Naqshbandi Imam in Daghestan. End of Muslim resistance in Chechnya and Daghestan. | |
| 1859 | Death of Muhammed al Sanusi, Reformer, Sufi Shaykh of Libya. | |
| 1860 | Alhajj Omar resists French colonization in Sene-Gambia. | |
| 1861 | American Civil War (1861-65). The price of Egyptian cotton soars in world markets. | |
| 1863 | Abraham Lincoln proclaims the abolition of slavery. | |
| 1869 | The Suez Canal opens with much fanfare. | |
| The price of Egyptian cotton drops precipitously. Egyptian public debt mounts. | ||
| Tunisia falters on debt payments to European bankers. The International Debt Commission for Tunisia assumes control over Tunisian finances. | ||
| 1871 | A unified Germany emerges as the most powerful continental power in Europe. | |
| 1873 | The Dutch capture the Kingdom of Acheh in Sumatra. Beginning of Dutch colonial rule in Indonesia. | |
| 1874 | Syed Ahmed Khan founds the Aligarh College in India. | |
| 1875 | Egypt sells off its share in the Suez Canal Company to the British to partially offset its debts. | |
| 1876 | Abdul Hamid II becomes the Ottoman Sultan and Caliph. He starts consolidation of ties with Muslim peoples worldwide. | |
| Egypt falters on debt payments. Britain and France appoint a Commission on Egyptian Public Debt with the power to confiscate revenues. | ||
| 1877 | Russia invades the Ottoman Empire (1877-78). Russian troops advance to within ten miles of Istanbul and dictate capitulation terms to the Turks at the Treaty of San Stefano. | |
| 1878 | Egypt is forced by Britain and France to accept international control over her finances. | |
| Treaty of Berlin results in effective dissolution of the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans. | ||
| Britain occupies Cyprus. | ||
| 1879 | Britain and France force Khedive Ismail Pasha of Egypt to abdicate in favor of his son Tawfiq Pasha. Sultan Abdul Hamid acquiesces in the abdication. | |
| 1880 | The French, in violation of the Treaty of Berlin, occupy Tunisia and declare it a “protectorate”. | |
| 1881 | Egyptian nationalists under Ahmed Torabi Pasha stage protests against foreign control. | |
| 1882 | The British bombard Alexandria into submission, defeat the Egyptians at the Battle of Tel el Kabir and occupy Cairo. | |
| The Mahdi seizes Khartoum and establishes a Caliphate in the Sudan. | ||
| 1885 | The British storm Khartoum. Death of al Mahdi of the Sudan. | |
| An Englishman, Allan Hume, founds the Indian National Congress. | ||
| 1888 | Ghulam Mirza Ahmed starts the Ahmadiya schism in Punjab, India. The movement draws strong opposition from the ulema. | |
| 1891 | The Tobacco Concession touches off an uproar in Persia. Peaceful boycott of tobacco, under a fatwa from Hajji Mirza Hassan Shirazi, forces the Shah to rescind the Concession. | |
| 1896 | Nasiruddin Shah of Persia is assassinated. | |
| 1901 | Abdul Aziz ibn Saud captures Riyadh. | |
| 1906 | All India Muslim League is founded. | |
| 1907 | Death of Muzaffaruddin Shah of Persia. His son Muhammed Ali Mirza becomes the Shah. The first Majlis is elected in Persia. | |
| The Young Turks Movement in Turkey gathers momentum. | ||
| 1908 | Austria-Hungary annexes Bosnia-Herzegovina. | |
| Constitutional revolution in Persia. Muhammed Ali Shah of Persia is deposed. His young son Ahmed Mirza becomes the Shah. | ||
| 1909 | Sultan Abdul Hamid II is deposed by the Young Turks. | |
| Mehmet V becomes the Sultan. | ||
| 1911 | The Sanusi brotherhood resists the Italian invasion of Libya. | |
| 1912 | Muhammadiya movement is organized in Indonesia. | |
| Egypt becomes a British protectorate. | ||
| 1913 | The Balkan war begins. Serbia, Greece and Bulgaria invade Ottoman territories. Albania becomes independent. The Ottomans are forced to withdraw from most of the Balkans. | |
| 1914 | A Serb in Sarajevo murders Prince Francis Ferdinand of Austria. Austria declares war on Serbia. | |
| Russia declares war on Austria. | ||
| Germany declares war on Russia. | ||
| France and England declare war on Germany. | ||
| The Triple Entente powers (Britain, France and Russia) declare war on the Ottomans. | ||
| Beginning of World War I. | ||
| 1915 | The Ottomans contain British advances in Iraq and beat back attempts to capture Baghdad and Istanbul. | |
| 1916 | The British promise to set up a unified Arab state. | |
| Sharif Hussain declares himself king of Hejaz, attacks Ottoman garrisons in Arabia. | ||
| Lawrence of Arabia, a British intelligence officer, works with the Arabs. | ||
| The Sykes-Picot agreement divides up the Ottoman territories between England, France, Russia, Greece and Italy. | ||
| 1917 | Anglo Indian troops under Allenby capture Baghdad and Jerusalem. | |
| The Balfour Declaration promises to set up a Jewish homeland in Palestine. | ||
| The French take Beirut. | ||
| Germany releases the Bolshevik leader Lenin to pressure Russia to drop out of the War. | ||
| The United States enters the War. | ||
| The Russian army begins to collapse on the western front. The October Revolution brings the Bolsheviks to power. Russia pulls out of the War. | ||
| 1918 | Mehmet VI becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| Damascus falls to British Forces. | ||
| Germany and the Ottoman Empire capitulate. End of World War I. | ||
| The Wafd movement starts in Egypt. | ||
| 1919 | The victorious allies partition the Ottoman Empire. | |
| Greece invades Anatolia. | ||
| 1920 | French mandate over Syria. | |
| British mandate over Iraq and Palestine. | ||
| The Greeks capture Alashehir, Bahkesir, Bandarma and Bursa. | ||
| The Turks stop the Greeks at the Battle of Ankara. | ||
| 1921 | The British appoint Abdullah, son of Sharif Hussain, as emir of Trans Jordan. | |
| Faisal, another son of Hussain, is appointed emir of Iraq. | ||
| The Turks are victorious over the Greeks at the Battle of the Sakarya River. Greece retreats from Anatolia. | ||
| 1922 | Abdul Mecit II becomes Ottoman Sultan. | |
| Mustafa Kemal becomes President of the Republic of Turkey. | ||
| 1924 1927 1928 1941 1945 1945-60s 1947 1957 1960s 1979 late 1990s back to top 2001 2003 |
The Turkish National Assembly abolishes the Caliphate.
|
|
* Submitted to the Encyclopedia of Islamic History (www.historyofislam.com) on March 1, 1995.
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________
Falkland Islands(UK) : Stanley
South America
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
back to top
_______________________________________________













